Phosphorylated ribosomal S6 (p-rpS6) as a post-treatment indicator of HER2 signalling targeted drug resistance
- PMID: 26329528
- PMCID: PMC7447531
- DOI: 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1068865
Phosphorylated ribosomal S6 (p-rpS6) as a post-treatment indicator of HER2 signalling targeted drug resistance
Abstract
Objective: To identify clinically relevant predictive biomarkers of trastuzumab resistance.
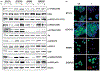
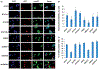
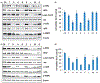
Material and methods: MTT, FACS assays, immunoblotting and immunocytochemistry were used to phenotypically characterize drug responses of two cell models BT474R and SKBR3R. Student's t-test and Spearman's correlation were applied for statistic analysis.
Results: The activity of a downstream effector of the HER2 pathway phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 (p-rpS6), was suppressed by trastuzumab in the parental cell lines yet remained unchanged in the resistant cells following treatment. The level of p-rpS6 was inversely correlated to the drug induced growth inhibition of trastuzumab-resistant cells when they are treated with selected HER2 targeting drugs.
Conclusion: p-rpS6 is a robust post-treatment indicator of HER2 pathway-targeted therapy resistance.
Keywords: Biomarker; breast cancer; cell model; drug response; trastuzumab resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures
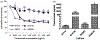


References
-
- Blackwell KL, Burstein HJ, Storniolo AM, et al. (2012). Overall survival benefit with lapatinib in combination with trastuzumab for patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer: final results from the EGF104900 Study. J Clin Oncol 30:2585–92. - PubMed
-
- Bottini A, Berruti A, Bersiga A, et al. (2000). p53 but not bcl-2 immunostaining is predictive of poor clinical complete response to primary chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 6:2751–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
