Pasiflora proteins are novel core components of the septate junction
- PMID: 26329602
- PMCID: PMC4582180
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.119412
Pasiflora proteins are novel core components of the septate junction
Abstract
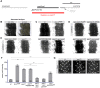
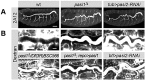
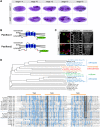
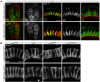
Epithelial sheets play essential roles as selective barriers insulating the body from the environment and establishing distinct chemical compartments within it. In invertebrate epithelia, septate junctions (SJs) consist of large multi-protein complexes that localize at the apicolateral membrane and mediate barrier function. Here, we report the identification of two novel SJ components, Pasiflora1 and Pasiflora2, through a genome-wide glial RNAi screen in Drosophila. Pasiflora mutants show permeable blood-brain and tracheal barriers, overelongated tracheal tubes and mislocalization of SJ proteins. Consistent with the observed phenotypes, the genes are co-expressed in embryonic epithelia and glia and are required cell-autonomously to exert their function. Pasiflora1 and Pasiflora2 belong to a previously uncharacterized family of tetraspan membrane proteins conserved across the protostome-deuterostome divide. Both proteins localize at SJs and their apicolateral membrane accumulation depends on other complex components. In fluorescence recovery after photobleaching experiments we demonstrate that pasiflora proteins are core SJ components as they are required for complex formation and exhibit restricted mobility within the membrane of wild-type epithelial cells, but rapid diffusion in cells with disrupted SJs. Taken together, our results show that Pasiflora1 and Pasiflora2 are novel integral components of the SJ and implicate a new family of tetraspan proteins in the function of these ancient and crucial cell junctions.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Drosophila; Epithelia; Septate junction; Trachea.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Baumgartner S., Littleton J. T., Broadie K., Bhat M. A., Harbecke R., Lengyel J. A., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Prokop A. and Bellen H. J. (1996). A Drosophila neurexin is required for septate junction and blood-nerve barrier formation and function. Cell 87, 1059-1068. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81800-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cording J., Berg J., Kading N., Bellmann C., Tscheik C., Westphal J. K., Milatz S., Gunzel D., Wolburg H., Piontek J., et al. (2013). In tight junctions, claudins regulate the interactions between occludin, tricellulin and marvelD3, which, inversely, modulate claudin oligomerization. J. Cell Sci. 126, 554-564. 10.1242/jcs.114306 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

