BRAF mutation testing with a rapid, fully integrated molecular diagnostics system
- PMID: 26330075
- PMCID: PMC4694960
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4723
BRAF mutation testing with a rapid, fully integrated molecular diagnostics system
Abstract
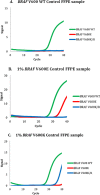
Fast and accurate diagnostic systems are needed for further implementation of precision therapy of BRAF-mutant and other cancers. The novel IdyllaTMBRAF Mutation Test has high sensitivity and shorter turnaround times compared to other methods. We used Idylla to detect BRAF V600 mutations in archived formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumor samples and compared these results with those obtained using the cobas 4800 BRAF V600 Mutation Test or MiSeq deep sequencing system and with those obtained by a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)-certified laboratory employing polymerase chain reaction-based sequencing, mass spectrometric detection, or next-generation sequencing. In one set of 60 FFPE tumor samples (15 with BRAF mutations per Idylla), the Idylla and cobas results had an agreement of 97%. Idylla detected BRAF V600 mutations in two additional samples. The Idylla and MiSeq results had 100% concordance. In a separate set of 100 FFPE tumor samples (64 with BRAF mutation per Idylla), the Idylla and CLIA-certified laboratory results demonstrated an agreement of 96% even though the tests were not performed simultaneously and different FFPE blocks had to be used for 9 cases. The IdyllaTMBRAF Mutation Test produced results quickly (sample to results time was about 90 minutes with about 2 minutes of hands on time) and the closed nature of the cartridge eliminates the risk of PCR contamination. In conclusion, our observations demonstrate that the Idylla test is rapid and has high concordance with other routinely used but more complex BRAF mutation-detecting tests.
Keywords: BRAF; integrated; qPCR; rapid.
Conflict of interest statement
Filip Janku has research support from Novartis, Biocartis, Trovagene, and Foundation Medicine. Bart Claes, Martin Reijans, Geert Maertens, and Erwin Sablon are employees of Biocartis NV, and Benoit Devogelaere was previously employed by Biocartis NV. Mark Kockx and Isabelle Vanden Bempt are employees of HistoGeneX NV. Razelle Kurzrock has research support from EMD Serono, Genentech, Foundation Medicine and Pfizer, consultantship fees from SEquenom, and ownership interest in RScueRx.
Figures
References
-
- Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the bcr-abl tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1031–7. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials