BA-j as a novel CDK1 inhibitor selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells by regulating ROS
- PMID: 26330167
- PMCID: PMC4557050
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13626
BA-j as a novel CDK1 inhibitor selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells by regulating ROS
Abstract
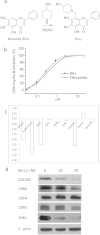
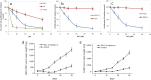
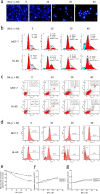
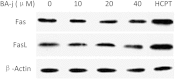
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) is the only necessary CDK in cell proliferation and a novel target in the development of anticancer drugs. 8-Hydroxypiperidinemethyl-baicalein (BA-j) is a novel selective CDK1 inhibitor with broad spectrum anti-cancer activity (IC50 12.3 μM) and 2 tumor xenografts. Because of the differential mechanisms controlling redox-states in normal and cancer cells, BA-j can capture oxygen free radicals ((·)O2(-)) and selectively increase the level of H2O2 in cancer cells, thereby specifically oxidize and activate the intrinsic apoptosis pathway bypassing the extrinsic death receptor pathway, thus inducing apoptosis in cancer cells rather than in normal cells. BA-j is different from cytotoxic anticancer drugs which can activate both the intrinsic apoptosis pathway and the extrinsic death receptor pathway, and therefore harm normal cells while killing cancer cells. The molecular and biochemical mechanisms of reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulation suggest that BA-j may be developed into a novel anticancer agent.
Figures
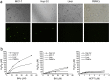
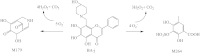
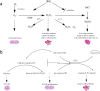
References
-
- Santamaria D. et al. Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle. Nature 448, 811–815 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Malumbres M. & Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 9, 153–166 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Diaz-Padilla I., Siu L. L. & Duran I. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors as potential targeted anticancer agents. Invest New Drug 27, 586–594 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Rizzolio F., Tuccinardi T., Caligiuri I., Lucchetti C. & Giordano A. CDK inhibitors: from the bench to clinical trials. Curr Drug Targets 11, 279–290 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Wesierska-Gadek J., Maurer M., Zulehner N. & Komina O. Whether to target single or multiple CDKs for therapy? That is the question. J Cell Physiol 226, 341–349 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

