Bacteriophage-mediated Glucosylation Can Modify Lipopolysaccharide O-Antigens Synthesized by an ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter-dependent Assembly Mechanism
- PMID: 26330553
- PMCID: PMC4646201
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.660803
Bacteriophage-mediated Glucosylation Can Modify Lipopolysaccharide O-Antigens Synthesized by an ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter-dependent Assembly Mechanism
Abstract
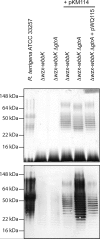
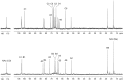
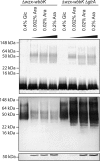
Lysogenic bacteriophages may encode enzymes that modify the structures of lipopolysaccharide O-antigen glycans, altering the structure of the bacteriophage receptor and resulting in serotype conversion. This can enhance virulence and has implications for antigenic diversity and vaccine development. Side chain glucosylation is a common modification strategy found in a number of bacterial species. To date, glucosylation has only been observed in O-antigens synthesized by Wzy-dependent pathways, one of the two most prevalent O-antigen synthesis systems. Here we exploited a heterologous system to study the glucosylation potential of a model O-antigen produced in an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter-dependent system. Although O-antigen production is cryptic in Escherichia coli K-12, because of a mutation in the synthesis genes, it possesses a prophage glucosylation cluster, which modifies the GlcNAc residue in an α-l-Rha-(1→3)-d-GlcNAc motif found in the original O16 antigen. Raoultella terrigena ATCC 33257 produces an O-antigen possessing the same disaccharide motif, but its assembly uses an ABC transporter-dependent system. E. coli harboring the R. terrigena O-antigen biosynthesis genes produced an O-antigen displaying reduced reactivity toward antisera raised against the native R. terrigena repeat structure, indicative of an altered chemical structure. Structural determination using NMR revealed the addition of glucose side chains to the repeat units. O-antigen modification was dependent on a functional ABC transporter, consistent with modification in the periplasm, and was eliminated by deletion of the glucosylation genes from the E. coli chromosome, restoring native level antisera sensitivity and structure. There are therefore no intrinsic mechanistic barriers for bacteriophage-mediated O-antigen glucosylation in ABC transporter-dependent pathways.
Keywords: ABC transporter; O-antigen; bacteriophage; biosynthesis; glycosylation; lipopolysaccharide (LPS); nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); outer membrane; polysaccharide.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Substrate recognition by a carbohydrate-binding module in the prototypical ABC transporter for lipopolysaccharide O-antigen from Escherichia coli O9a.J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 11;294(41):14978-14990. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010323. Epub 2019 Aug 15. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31416837 Free PMC article.
-
The Klebsiella pneumoniae O12 ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter Recognizes the Terminal Residue of Its O-antigen Polysaccharide Substrate.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9748-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.719344. Epub 2016 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26934919 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of lipopolysaccharide O-antigens by ABC transporter-dependent pathways.Carbohydr Res. 2012 Jul 15;356:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2012.02.027. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Carbohydr Res. 2012. PMID: 22475157 Review.
-
Identification of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa O17 and O15 O-Specific Antigen Biosynthesis Loci Reveals an ABC Transporter-Dependent Synthesis Pathway and Mechanisms of Genetic Diversity.J Bacteriol. 2020 Sep 8;202(19):e00347-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00347-20. Print 2020 Sep 8. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32690555 Free PMC article.
-
O-antigen structural variation: mechanisms and possible roles in animal/plant-microbe interactions.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002 Mar;26(1):17-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2002.tb00597.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12007641 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and profiling of novel metagenome assembled uncultivated virus genomes from human gut.Virol J. 2025 Jul 25;22(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02739-1. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40713701 Free PMC article.
-
Yersinia ruckeri Isolates Recovered from Diseased Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) in Scotland Are More Diverse than Those from Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Represent Distinct Subpopulations.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Sep 16;82(19):5785-94. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01173-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27451448 Free PMC article.
-
Completing the BASEL phage collection to unlock hidden diversity for systematic exploration of phage-host interactions.PLoS Biol. 2025 Apr 7;23(4):e3003063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003063. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 40193529 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide O-antigens-bacterial glycans made to measure.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 31;295(31):10593-10609. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.009402. Epub 2020 May 18. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32424042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wzx flippases exhibiting complex O-unit preferences require a new model for Wzx-substrate interactions.Microbiologyopen. 2019 Mar;8(3):e00655. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.655. Epub 2018 Jun 10. Microbiologyopen. 2019. PMID: 29888516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stenutz R., Weintraub A., Widmalm G. (2006) The structures of Escherichia coli O-polysaccharide antigens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30, 382–403 - PubMed
-
- Rojas-Macias M. A., Ståhle J., Lütteke T., Widmalm G. (2015) Development of the ECODAB into a relational database for Escherichia coli O-antigens and other bacterial polysaccharides. Glycobiology 25, 341–347 - PubMed
-
- Lundborg M., Modhukur V., Widmalm G. (2010) Glycosyltransferase functions of E. coli O-antigens. Glycobiology. 20, 366–368 - PubMed
-
- Allison G. E., Verma N. K. (2000) Serotype-converting bacteriophages and O-antigen modification in Shigella flexneri. Trends Microbiol. 8, 17–23 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

