A Higher Angiogenin Expression is Associated With a Nonnuclear Maspin Location in Laryngeal Carcinoma
- PMID: 26330923
- PMCID: PMC4553359
- DOI: 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.268
A Higher Angiogenin Expression is Associated With a Nonnuclear Maspin Location in Laryngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: In numerous malignancies, angiogenin (ANG) and Maspin are important proangiogenic and antiangiogenic regulators, respectively. The aim of this study was to identify potential relationships between the biological roles of these two proteins in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC).
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining for ANG and Maspin was performed on specimens from 76 consecutive LSCC patients treated with surgery alone, considering the subcellular pattern of Maspin expression. Univariate and multivariate statistical models were used for prognostic purposes.
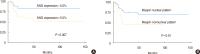
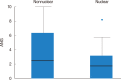
Results: On univariate analysis, a different level of ANG expression was seen for patients stratified by subcellular Maspin expression pattern: the mean ANG expression was higher in cases with a nonnuclear MASPIN expression than in those with a nuclear pattern (P=0.002). Disease-free survival (DFS; in months) differed significantly when patients were stratified by N stage (P=0.01). Patients whose Maspin expression was nonnuclear (i.e., it was cytoplasmic or there was none) had a significantly higher recurrence rate (P<0.001), and shorter DFS (P=0.01) than those with a nuclear Maspin pattern. The mean ANG expression was significantly higher in cases with loco-regional recurrent disease (P=0.007); and patients with an ANG expression ≥5.0% had a significantly shorter DFS than those with an ANG expression <5.0% (P=0.007). On multivariate analysis, ANG expression ≥5.0% was a significant, independent, negative prognostic factor in terms of DFS (P=0.041).
Conclusion: Our results support the hypothesis that a higher ANG expression is associated with a nonnuclear Maspin expression pattern in patients with LSCC. Further studies are needed to clarify the relationship between the ANG and Maspin pathways, and their potential diagnostic and therapeutic role in LSCC.
Keywords: Angiogenin; Intracellular Space; Laryngeal Neoplasms; Prognosis; SERPIN-B5.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Tello-Montoliu A, Patel JV, Lip GY. Angiogenin: a review of the pathophysiology and potential clinical applications. J Thromb Haemost. 2006 Sep;4(9):1864–1874. - PubMed
-
- Kishimoto K, Liu S, Tsuji T, Olson KA, Hu GF. Endogenous angiogenin in endothelial cells is a general requirement for cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Oncogene. 2005 Jan;24(3):445–456. - PubMed
-
- Gao X, Xu Z. Mechanisms of action of angiogenin. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 008 Jul;40(7):619–624. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Shi HY, Zhang M. Targeted expression of maspin in tumor vasculatures induces endothelial cell apoptosis. Oncogene. 2005 Mar;24(12):2008–2019. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

