Preclinical evaluation of a novel abluminal surface coated sirolimus eluting stent with biodegradable polymer matrix
- PMID: 26331109
- PMCID: PMC4536475
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-3652.2015.06.01
Preclinical evaluation of a novel abluminal surface coated sirolimus eluting stent with biodegradable polymer matrix
Abstract
Background: Second generation of drug eluting stents (DES) has attempted to improve safety using abluminal sirolimus drug delivery with biodegradable polymers matrix. The present preclinical study was designed to investigate the safety and efficacy profile of Abluminus™ stents (SES). This is a new coronary stent with sirolimus and biodegradable polymer matrix coated on abluminal stent and balloon surface.
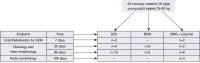
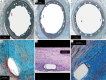
Methods: SES were compared with two controls: bare metal stent (BMS) and BMS + polymer coated stents (PC). All devices (40 stents) were implanted in porcine coronary arteries with primary endpoint of endothelialization at 7 days and subsequent histological and morphometric evaluations at 7, 30 and 90 days.
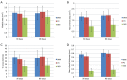
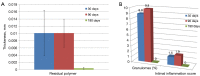
Results: Early endothelialization at seven days was complete in all stents. Histology at 30 days revealed minimum inflammation in all groups and increased at 90 days in PC group while it was absent at 180 days. Thirty day morphometry showed significantly reduction of neointimal area in Abluminus™ (SES 0.96±0.48 mm(2); BMS 1.83±0.34 mm(2); PC 1.76±0.55 mm(2); P<0.05); after 90 days neointimal area was 1.10±0.54 mm(2) for SES; 1.92±0.36 mm(2) for BMS; and 1.94±0.48 mm(2) for PC; P<0.05). Neointimal thickness at 30 and 90 days respectively was 0.15±0.07 and 0.18±0.10 mm for SES, 0.57±0.08 and 0.61±0.09 mm for BMS and 0.52±0.09 and 0.59±0.08 mm, P<0.001 for PC group.
Conclusions: The most significant experimental evidence appears to be earlier endothelialization at 7 days for SES which led to safety of the device. Efficacy of the device was also observed by a reduced neointimal thickness and minimized inflammatory score at all follow-ups. Termination of antiplatelet at 30 days has not shown any further complications. Polymer thickness was almost in negligible amount at 180 days with no inflammation.
Keywords: Stent; abluminal; bio-degradable polymer; restenosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative preclinical evaluation of a polymer-free sirolimus-eluting stent in porcine coronary arteries.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753944719826335. doi: 10.1177/1753944719826335. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 30803407 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer-free biolimus a9-coated stent demonstrates more sustained intimal inhibition, improved healing, and reduced inflammation compared with a polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting cypher stent in a porcine model.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010 Apr;3(2):174-83. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.109.877522. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010. PMID: 20407114
-
Cre8™ coronary stent: preclinical in vivo assessment of a new generation polymer-free DES with Amphilimus™ formulation.EuroIntervention. 2012 Jan;7(9):1087-94. doi: 10.4244/EIJV7I9A173. EuroIntervention. 2012. PMID: 22130128
-
Evaluation of the MiStent sustained sirolimus eluting biodegradable polymer coated stent for the treatment of coronary artery disease: does uniform sustained abluminal drug release result in earlier strut coverage and better safety profile?Expert Rev Med Devices. 2017 May;14(5):325-334. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2017.1318057. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2017. PMID: 28402204 Review.
-
The significance of preclinical evaluation of sirolimus-, paclitaxel-, and zotarolimus-eluting stents.Am J Cardiol. 2007 Oct 22;100(8B):36M-44M. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.08.020. Am J Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17950831 Review.
Cited by
-
Early thrombogenicity of coronary stents: comparison of bioresorbable polymer sirolimus-eluting and bare metal stents in an aortic rat model.Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Jun 15;10(2):72-83. eCollection 2020. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32685265 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Safety and Efficacy of Novel Sirolimus-Eluting Stent Incorporating Properties of Drug Coating Balloon Among Real World Patients Focusing Younger Population (<35 years).J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2021 Oct 29;33(4):321-331. doi: 10.37616/2212-5043.1279. eCollection 2021. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 35083124 Free PMC article.
-
Two-year safety and efficacy of Indigenous Abluminus Sirolimus Eluting Stent. Does it differ amongst diabetics? - Data from en-ABLe- REGISTRY.J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2021;13(2):162-168. doi: 10.34172/jcvtr.2021.31. Epub 2021 May 19. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2021. PMID: 34326971 Free PMC article.
-
A Strategy for the In-Silico Assessment of Drug Eluting Stents: A Comparative Study for the Evaluation of Retinoic Acid as a Novel Drug Candidate for Drug Eluting Stents.IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2024 May 16;6:1-9. doi: 10.1109/OJEMB.2024.3402057. eCollection 2025. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39564556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertrand OF, Sipehia R, Mongrain R, et al. Biocompatibility aspects of new stent technology. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;32:562-71. - PubMed
-
- Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Ladich E, et al. Drug-eluting stent safety: findings from preclinical studies. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2008;6:1379-91. - PubMed
-
- Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Joner M, et al. Delayed arterial healing and increased late stent thrombosis at culprit sites after drug-eluting stent placement for acute myocardial infarction patients: an autopsy study. Circulation 2008;118:1138-45. - PubMed
-
- Virmani R, Farb A, Guagliumi G, et al. Drug-eluting stents: caution and concerns for long-term outcome. Coron Artery Dis 2004;15:313-8. - PubMed
-
- Hezi-Yamit A, Sullivan C, Wong J, et al. Impact of polymer hydrophilicity on biocompatibility: implication for DES polymer design. J Biomed Mater Res A 2009;90:133-41. - PubMed
