Lytic Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii: 15 Years Later
- PMID: 26332089
- PMCID: PMC4659696
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-micro-091014-104100
Lytic Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii: 15 Years Later
Abstract
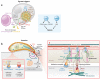
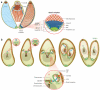
Toxoplasmosis is the clinical and pathological consequence of acute infection with the obligate intracellular apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Symptoms result from tissue destruction that accompanies lytic parasite growth. This review updates current understanding of the host cell invasion, parasite replication, and eventual egress that constitute the lytic cycle, as well as the ways T. gondii manipulates host cells to ensure its survival. Since the publication of a previous iteration of this review 15 years ago, important advances have been made in our molecular understanding of parasite growth and mechanisms of host cell egress, and knowledge of the parasite's manipulation of the host has rapidly progressed. Here we cover molecular advances and current conceptual frameworks that include each of these topics, with an eye to what may be known 15 years from now.
Keywords: Apicomplexa; IRG; egress; endodyogeny; inflammasome; invasion.
Figures

References
References cited
Annotated key references
-
- Moudy R, Manning TJ, Beckers CJ. The loss of cytoplasmic potassium upon host cell breakdown triggers egress of Toxoplasma gondii. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41492–501. First comphrehensive analysis of the egress mechanism by innovative assays. - PubMed
-
- Lourido S, Shuman J, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Hui R, Sibley LD. Calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 is an essential regulator of exocytosis in Toxoplasma. Nature. 2010;465:359–62. First proof of a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase, a protein family absent from mammals, with an essential role in invasion. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meissner M, Schluter D, Soldati D. Role of Toxoplasma gondii myosin A in powering parasite gliding and host cell invasion. Science. 2002;298:837–40. Shows that Myosin A, a class XIVa myosin, is the main motor driving motility and invasion. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI069986/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI069986/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03AI107475/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AI107475/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI081924/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI107257/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI099658/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI107257/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32AI108251/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI108251/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI081924/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI099658/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RRP 12-175/HX/HSRD VA/United States
- R21 AI081220/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

