Promoter-Dependent Translation Controlled by p54nrb and hnRNPM during Myoblast Differentiation
- PMID: 26332123
- PMCID: PMC4558007
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136466
Promoter-Dependent Translation Controlled by p54nrb and hnRNPM during Myoblast Differentiation
Abstract
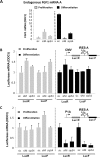
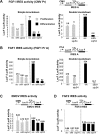
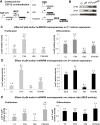
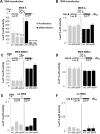
Fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) is induced during myoblast differentiation at both transcriptional and translational levels. Here, we identify hnRNPM and p54nrb/NONO present in protein complexes bound to the FGF1 promoter and to the mRNA internal ribosome entry site (IRES). Knockdown or overexpression of these proteins indicate that they cooperate in activating IRES-dependent translation during myoblast differentiation, in a promoter-dependent manner. Importantly, mRNA transfection and promoter deletion experiments clearly demonstrate the impact of the FGF1 promoter on the activation of IRES-dependent translation via p54nrb and hnRNPM. Accordingly, knockdown of either p54 or hnRNPM also blocks endogenous FGF1 induction and myotube formation, demonstrating the physiological relevance of this mechanism and the role of these two proteins in myogenesis. Our study demonstrates the cooperative function of hnRNPM and p54nrb as regulators of IRES-dependent translation and indicates the involvement of a promoter-dependent mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Maniatis T, Reed R. An extensive network of coupling among gene expression machines. Nature. 2002. April 4;416(6880):499–506. . - PubMed
-
- Madiai F, Hackshaw KV, Chiu IM. Characterization of the entire transcription unit of the mouse fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF-1) gene. Tissue-specific expression of the FGF-1.A mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1999. April 23;274(17):11937–44. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

