Support surfaces for pressure ulcer prevention
- PMID: 26333288
- PMCID: PMC7075275
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001735.pub5
Support surfaces for pressure ulcer prevention
Abstract
Background: Pressure ulcers (i.e. bedsores, pressure sores, pressure injuries, decubitus ulcers) are areas of localised damage to the skin and underlying tissue. They are common in the elderly and immobile, and costly in financial and human terms. Pressure-relieving support surfaces (i.e. beds, mattresses, seat cushions etc) are used to help prevent ulcer development.
Objectives: This systematic review seeks to establish:(1) the extent to which pressure-relieving support surfaces reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers compared with standard support surfaces, and,(2) their comparative effectiveness in ulcer prevention.
Search methods: In April 2015, for this fourth update we searched The Cochrane Wounds Group Specialised Register (searched 15 April 2015) which includes the results of regular searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINAHL and The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2015, Issue 3).
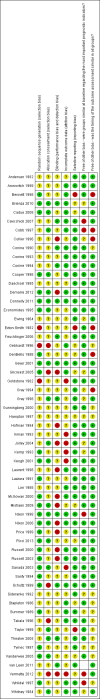
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-randomised trials, published or unpublished, that assessed the effects of any support surface for prevention of pressure ulcers, in any patient group or setting which measured pressure ulcer incidence. Trials reporting only proxy outcomes (e.g. interface pressure) were excluded. Two review authors independently selected trials.
Data collection and analysis: Data were extracted by one review author and checked by another. Where appropriate, estimates from similar trials were pooled for meta-analysis.
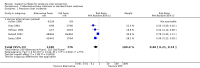
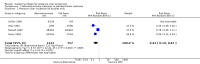
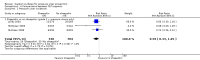
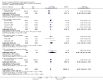
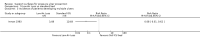
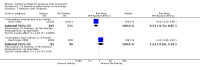
Main results: For this fourth update six new trials were included, bringing the total of included trials to 59.Foam alternatives to standard hospital foam mattresses reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers in people at risk (RR 0.40 95% CI 0.21 to 0.74). The relative merits of alternating- and constant low-pressure devices are unclear. One high-quality trial suggested that alternating-pressure mattresses may be more cost effective than alternating-pressure overlays in a UK context.Pressure-relieving overlays on the operating table reduce postoperative pressure ulcer incidence, although two trials indicated that foam overlays caused adverse skin changes. Meta-analysis of three trials suggest that Australian standard medical sheepskins prevent pressure ulcers (RR 0.56 95% CI 0.32 to 0.97).
Authors' conclusions: People at high risk of developing pressure ulcers should use higher-specification foam mattresses rather than standard hospital foam mattresses. The relative merits of higher-specification constant low-pressure and alternating-pressure support surfaces for preventing pressure ulcers are unclear, but alternating-pressure mattresses may be more cost effective than alternating-pressure overlays in a UK context. Medical grade sheepskins are associated with a decrease in pressure ulcer development. Organisations might consider the use of some forms of pressure relief for high risk patients in the operating theatre.
Conflict of interest statement
Nicky Cullum was the Principal Investigator in the PRESSURE Trial, one of the trials included in this review (Nixon 2006), however, she was not involved in the data extraction or analysis for this trial. Kinetic Concepts Inc (KCI) supplied (free of charge) three VAC therapy units and starter packs for use in a pilot RCT of negative pressure wound therapy for pressure ulcers. They also provided product training, support and access to the KCI 24hr advice service for clinical and technical queries. However KCI had no input into the design, conduct, analysis or reporting of that research or this review which is not concerned with this technology. E McInnes: no interests declared. A Jammali‐Blasi: no interests declared. SEM Bell‐Syer: no interests declared. JC Dumville: no interests declared. V Middleton: was funded as research assistant by Nursing Research Institute (Australian Catholic University) to assist with this review.
Figures












Update of
-
Support surfaces for pressure ulcer prevention.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Apr 13;(4):CD001735. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001735.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 03;(9):CD001735. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001735.pub5. PMID: 21491384 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Andersen 1982 {published data only}
-
- Andersen KE, Jensen O, Kvorning SA, Bach E. Decubitus prophylaxis: a prospective trial on the efficiency of alternating pressure air mattresses and water mattresses. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica (Stockholm) 1982;63(3):227‐30. - PubMed
Aronovitch 1999 {published data only}
-
- Aronovitch SA, Wilber M, Slezak S, Martin T, Utter D. A comparative study of an alternating air mattress for the prevention of pressure ulcers in surgical patients. Ostomy/Wound Management 1999;45(3):34‐40, 42‐4. - PubMed
Bennett 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bennett RG, Baran PJ, DeVone LV, Bacetti H, Kristo B, Tayback M, et al. Low airloss hydrotherapy versus standard care for incontinent hospitalized patients [see comments]. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1998;46(5):569‐76. - PubMed
Brienza 2010 {published data only}
Cadue 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cadue J‐F, Karolewicz S, Tardy C, Barrault C, Robert R, Pourrat O. Prevention of heel pressure sores with a foam body‐support device. A randomized controlled trial in a medical intensive care unit [Efficacite de supports anatomiques en mousse pour la prevention des escarres de talons]. Presse Medicale 2008;37(1 Pt 1):30‐6. - PubMed
Cavicchioli 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cavicchioli A, Carella G. Clinical effectiveness of a low‐tech versus high‐tech pressure redistributing mattress. Journal of Wound Care 2007;16(7):285‐9. - PubMed
Cobb 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cobb GA, Yoder LH, Warren JB. Pressure ulcers: patient outcomes on a KinAir bed or EHOB waffle mattress. TriService Nursing Research Program (TSNRP). Bethesda, Maryland, USA, 1997.
Collier 1996 {published data only}
-
- Collier ME. Pressure‐reducing mattresses. Journal of Wound Care 1996;5(5):207‐11. - PubMed
Conine 1990 {published data only}
-
- Conine TA, Daechsel D, Choi AK, Lau MS. Costs and acceptability of two special overlays for the prevention of pressure sores. Rehabilitation Nursing 1990;15(3):133‐7. - PubMed
-
- Conine TA, Daechsel D, Lau MS. The role of alternating air and silicore overlays in preventing decubitus ulcers. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1990;13(1):57‐65. - PubMed
Conine 1993 {published data only}
-
- Conine TA, Daeschel D, Hershler C. Pressure sore prophylaxis in elderly patients using slab foam or customised contoured foam wheelchair cushions. Occupational Therapy Journal of Research 1993;13(2):101‐16.
Conine 1994 {published data only}
-
- Conine TA, Hershler C, Daechsel D, Peel C, Pearson A. Pressure sore prophylaxis in elderly patients using polyurethane foam or Jay wheelchair cushions. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1994;17(2):123‐37. - PubMed
Cooper 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cooper PJ, Gray DG, Mollison J. A randomised controlled trial of two pressure reducing surfaces. Journal of Wound Care 1998;7(8):374‐6. - PubMed
Daechsel 1985 {published data only}
-
- Daechsel D, Conine TA. Special mattresses: effectiveness in preventing decubitus ulcers in chronic neurologic patients. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1985;66(4):246‐8. - PubMed
Demarre 2012 {published data only}
-
- Demarré L, Beeckman D, Vanderwee K, Defloor T, Grypdonck M, Verhaeghe S. Multi‐stage versus single‐stage inflation and deflation cycle for alternating low pressure air mattresses to prevent pressure ulcers in hospitalised patients: A randomised‐controlled clinical trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2012;49(4):416‐426. - PubMed
Donnelly 2011 {published data only}
-
- Donnelly J, Winder J, Kernohan WG, Stevenson M. An RCT to determine the effect of a heel elevation device in pressure ulcer prevention post‐hip fracture. Journal of Wound Care 2011;20(7):309‐318. - PubMed
Economides 1995 {published data only}
-
- Economides NG, Skoutakis VA, Carter CA, Smith VH. Evaluation of the effectiveness of two support surfaces following myocutaneous flap surgery. Advances in Wound Care 1995;8(1):49‐53. - PubMed
Ewing 1964 {published data only}
-
- Ewing MR, Garrow C, Presley TA, Ashley C, Kinsella NM. Further experiences in the use of sheep skins as an aid in nursing. The Australian Nurses' Journal 1964;Sept:215‐9.
Exton‐Smith 1982 {published data only}
-
- Exton‐Smith AN, Overstall PW, Wedgewood J, Wallace G. Use of the 'air wave system' to prevent pressure sores in hospital. The Lancet 1982;1(8284):1288‐90. - PubMed
Feuchtinger 2006 {published data only}
-
- Feuchtinger J. Preventing decubitus ulcer in heart surgery interventions: visco‐elastic foam layer on the operating room table — a study [Viskoelastische schaumstoffauflage auf dem operationstisch — eine studie]. Pflege Zeitschrift 2006;59(8):498‐501. - PubMed
-
- Feuchtinger J, Bie R, Dassen T, Halfens R. A 4‐cm thermoactive viscoelastic foam pad on the operating room table to prevent pressure ulcer during cardiac surgery. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2006;15(2):162‐7. - PubMed
Gebhardt 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gebhardt K. A randomized trial of alternating pressure (AP) and constant low pressure (CLP) supports for the prevention of pressure sores. Journal of Tissue Viability 1994;4(3):93.
-
- Gebhardt KS, Bliss MR, Winwright PL. A randomised controlled trial to compare the efficacy of alternating and constant low pressure supports for preventing pressure sores in an intensive care unit. Personal Communication 1994.
-
- Gebhardt KS, Bliss MR, Winwright PL, Thomas J. Pressure relieving supports in an ICU. Journal of Wound Care 1996;5(3):116‐21. - PubMed
Gentilello 1988 {published data only}
-
- Gentilello L, Thompson DA, Tonnesen AS, Hernandez D, Kapadia AS, Allen SJ, et al. Effect of a rotating bed on the incidence of pulmonary complications in critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine 1988;16(8):783‐6. - PubMed
Geyer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Geyer MJ, Brienza DM, Karg P, Trefler E, Kelsey S. A randomized control trial to evaluate pressure‐reducing seat cushions for elderly wheelchair users. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2001;14(3):120‐9. - PubMed
Gilcreast 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gilcreast DM, Warren JB, Yoder LH, Clark JJ, Wilson JA, Mays MZ. Research comparing three heel ulcer‐prevention devices. Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2005;32(2):112‐20. - PubMed
Goldstone 1982 {published data only}
-
- Goldstone L, Norris M, O'Reilly M, White J. A clinical trial of a bead bed system for the prevention of pressure sores in elderly orthopaedic patients. Journal of Advanced Nursing 1982;7(6):545‐8. - PubMed
Gray 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gray D. A randomised clinical trial of two foam mattresses. Aberdeen Royal Hospitals NHS Trust.
-
- Gray D. A randomised controlled trial of two foam mattresses. Journal of Tissue Viability 1994;4(3):92.
-
- Gray DG, Campbell M. A randomized clinical trial of two types of foam mattresses. Journal of Tissue Viability 1994;4(4):128‐32.
-
- Gray DG, Cooper PJ, Campbell M. A study of the performance of a pressure reducing foam mattress after three years of use. Journal of Tissue Viability 1998;8(3):9‐13. - PubMed
Gray 1998 {published data only}
-
- Gray D, Smith M. A randomized controlled trial of two pressure‐reducing foam mattresses. European Wound Management Association Conference; 1998 November; Harrogate, UK. 1998:4.
Gunningberg 2000 {published data only}
-
- Gunningberg L, Lindholm C, Carlsson M, Sjoden P‐O. Effect of visco‐elastic foam mattresses on the development of pressure ulcers in patients with hip fractures. Journal of Wound Care 2000;9(10):455‐60. - PubMed
Hampton 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hampton S. Evaluation of the new Cairwave Therapy System in one hospital trust. British Journal of Nursing 1997;6(3):167‐70. - PubMed
Hofman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hofman A, Geelkerken RH, Wille J, Hamming JJ, Hermans J, Breslau PJ. Pressure sores and pressure‐decreasing mattresses: controlled clinical trial. Lancet 1994;343(8897):568‐71. - PubMed
Inman 1993 {published data only}
-
- Inman KJ, Sibbald WJ, Rutledge FS, Clark BJ. Clinical utility and cost‐effectiveness of an air suspension bed in the prevention of pressure ulcers. JAMA 1993;269(9):1139‐43. - PubMed
Jolley 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jolley DJ, Wright R, McGowan S, Hickey MB, Campbell DA, Sinclair RD, et al. Preventing pressure ulcers with the Australian Medical Sheepskin: an open‐label randomised controlled trial. Medical Journal of Australia 2004;180(7):324‐7. - PubMed
Kemp 1993 {published data only}
-
- Kemp MG, Kopanke D, Tordecilla L, Fogg L, Shott S, Matthiesen V, et al. The role of support surfaces and patient attributes in preventing pressure ulcers in elderly patients. Research in Nursing and Health 1993;16(2):89‐96. - PubMed
Keogh 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dealey C, Keogh A. A randomised controlled trial comparing the effect of using an electric profiling bed with standard hospital bed for patients at high risk of pressure sore development. 10th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2000 18‐20 May; Stockholm, Sweden. 2000:30.
-
- Keogh A, Dealey C. Profiling beds versus standard hospital beds: effects on pressure ulcer incidence outcomes. Journal of Wound Care 2001;10(2):15‐9. - PubMed
Laurent 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- Laurent S. Effectiveness of pressure decreasing mattresses in cardiovascular surgery patients: a controlled clinical trial. 3rd European Conference for Nurse Managers, 1997 Oct; Brussels, Belgium. Brussels, 1998.
Lazzara 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lazzara DJ, Buschmann MBT. Prevention of pressure ulcers in elderly nursing home residents: are special support surfaces the answer?. Decubitus 1991;4(4):42‐6. - PubMed
Lim 1988 {published data only}
-
- Lim R, Sirett R, Conine TA, Daechsel D. Clinical trial of foam cushions in the prevention of decubitis ulcers in elderly patients. Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1988;25(2):19‐26. - PubMed
McGowan 2000 {published data only}
-
- McGowan S, Montgomery K, Jolley D, Wright R. [The role of sheepskins in preventing pressure ulcers in elderly orthopaedic patients]. First World Wound Healing Congress; 2000, 10‐13 September; Melbourne, Australia. 2000:108.
-
- McGowan S, Montgomery K, Jolley D, Wright R. The role of sheepskins in preventing pressure ulcers in elderly orthopaedic patients. Primary Intention 2000;8(4):1‐8.
Mistiaen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mistiaen P, Francke A, Achterberg W, Ament A, Halfens R, Huizinga J. Australian Medical Sheepskin is effective for the prevention of pressure ulcers [Australische Medische Schapenvacht effectief bij de preventie van stuitdecubitus]. Tijdschrift voor Ouderengeneeskunde 2009;5:186‐90.
Nixon 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bridel‐Nixon J, McElveney D, Brown J, Mason S. [Findings from a double‐triangular sequential‐design randomized clinical trial of a dry polymer pad]. European Wound Management Association Conference; 1997, 27‐29 April; Milan, Italy. London: Macmillan Magazines, 1997:20‐1.
-
- Bridel‐Nixon J, McElveney D, Brown J, Mason S. A randomized controlled trial using a double‐triangular sequential design: methodology and management issues. European Wound Management Association Conference; 1997, 27‐29 April; Milan, Italy. London: Macmillan Magazines, 1997:65‐6.
-
- Nixon J, McElvenny D, Mason S, Brown J, Bond S. A sequential randomised controlled trial comparing a dry visco‐elastic polymer pad and standard operating table mattress in the prevention of postoperative pressure sores. International Journal of Nursing Studies 1998;35(4):193‐203. - PubMed
Nixon 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nixon J, Cranny G, Iglesias C, Nelson EA, Hawkins K, Phillips A, et al. Randomised, controlled trial of alternating pressure mattresses compared with alternating pressure overlays for the prevention of pressure ulcers: PRESSURE (pressure relieving support surfaces) trial. BMJ 2006;332(7555):1413‐5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nixon J, Nelson EA, Cranny G, Iglesias CP, Hawkins K, Cullum NA, et al. Pressure relieving support surfaces: A randomised evaluation. Health Technology Assessment (Winchester, England) 2006;10(22):iii‐101. - PubMed
Price 1999 {published data only}
-
- Price P, Bale S, Newcombe R, Harding K. Challenging the pressure sore paradigm. Journal of Wound Care 1999;8(4):187‐90. - PubMed
Ricci 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ricci E, Roberto C, Ippolito A, Bianco A, Scalise MT. A new pressure‐relieving mattress overlay. European Wound Management Association Journal 2013;13(1):27‐32.
Russell 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dunlop V. Preliminary results of a randomised controlled study of a pressure ulcer prevention system. Advances in Wound Care 1998;11(3 suppl 1):14. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein S. A 7 day comparative randomized parallel single centre study to determine the safety and efficacy of the Micropulse system for the prevention of pressure ulcers. Micropulse 1997.
-
- Russell JA, Lichtenstein SL. Randomised controlled trial to determine the safety and efficacy of a multi‐cell pulsating dynamic mattress system in the prevention of pressure ulcers in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgery. Ostomy/Wound Management 2000;46(2):46‐51, 54‐5. - PubMed
Russell 2003 {published data only}
-
- Russell LJ, Reynolds TM, Park C, Rithalia S, Gonsalkorale M, Birch J, et al. Randomised clinical trial comparing CONFOR‐Med and standard hospital mattresses: results of the prevention of pressure ulcers study (PPUS‐1). Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2003;16(6):317‐27. - PubMed
Sanada 2003 {published data only}
-
- Matsui Y, Miyake S, KawasakiT, Konya C, Sugama J, Sanada H. Randomized controlled trial of a two layer type air cell mattress in the prevention of pressure ulcers. Japanese Journal of Pressure Ulcers 2001;3(3):331‐7.
-
- Sanada H, Sugama J, Matsui Y, Konya C, Kitagawa A, Okuwa M, et al. Randomised controlled trial to evaluate a new double‐layer air‐cell overlay for elderly patients requiring head elevation. Journal of Tissue Viability. 2003;13(3):112‐4, 116, 118 passim. - PubMed
Santy 1994 {published data only}
-
- Santy JE, Butler MK, Whyman JD. A comparison study of 6 types of hospital mattress to determine which most effectively reduces the incidence of pressure sores in elderly patients with hip fractures in a District General Hospital. Report to Northern & Yorkshire Regional Health Authority. 1994.
Schultz 1999 {published data only}
-
- Schultz A, Bien M, Dumond K, Brown K, Myers A. Etiology and incidence of pressure ulcers in surgical patients. AORN Journal 1999;70(3):434, 437‐40, 443‐9. - PubMed
-
- Schultz AA. Study results: prediction and prevention of pressure ulcers in surgical patients. Advances in Wound Care 1998;11(3 Suppl):11. - PubMed
Sideranko 1992 {published data only}
-
- Sideranko S, Quinn A. Burns K, Froman RD. Effects of position and mattress overlay on sacral and heel pressures in a clinical population. Research in Nursing and Health 1992;15(4):245‐51. - PubMed
Stapleton 1986 {published data only}
-
- Stapleton M. Preventing pressure sores ‐‐ an evaluation of three products... foam, ripple pads, and Spenco pads. Geriatric Nursing (London, England) 1986;6(2):23‐5. - PubMed
Summer 1989 {published data only}
-
- Summer WR, Curry P, Haponikm EF, Nelson S, Elston R. Continuous mechanical turning of intensive care unit patients shortens length of stay in some diagnostic‐related groups. Journal of Critical Care 1989;4:45‐53.
Takala 1996 {published data only}
-
- Takala J, Varmavuo S, Soppi E. Prevention of pressure sores in acute respiratory failure: a randomised controlled trial. Clinical Intensive Care 1996;7(5):228‐35.
Taylor 1999 {published data only}
-
- Taylor L. Evaluating the Pegasus Trinova: a data hierarchy approach. British Journal of Nursing 1999;8(12):771‐8. - PubMed
Theaker 2005 {published data only}
-
- Theaker C, Kuper M, Soni N. Pressure ulcer prevention in intensive care ‐ a randomised control trial of two pressure‐relieving devices. Anaesthesia 2005;60(4):395‐9. - PubMed
Tymec 1997 {published data only}
-
- Tymec AC, Pieper B, Vollman K. A comparison of two pressure relieving devices on the prevention of heel pressure ulcers. Advances in Wound Care 1997;10(1):39‐44. - PubMed
Vanderwee 2005 {published data only}
-
- Vanderwee K, Grypdonck MH, Defloor T. Effectiveness of an alternating pressure air mattress for the prevention of pressure ulcers. Age and Ageing 2005;34(3):261‐7. - PubMed
van Leen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Leen M, Hovius S, Neyens J, Halfens R, Schols J. Pressure relief, cold foam or static air? A single center, prospective, controlled randomized clinical trial in a dutch nursing home. Journal of TIssue Viability 2011;20:30‐34. - PubMed
Vermette 2012 {published data only}
-
- Vermette S, Reeves I, Lemaire J. Cost effectiveness of an air‐inflated static overlay for pressure ulcer prevention: A randomized controlled trial. WOUNDS 2012;24(8):207. - PubMed
Vyhlidal 1997 {published data only}
-
- Vyhlidal SK, Moxness D, Bosak KS, Meter FG, Bergstrom N. Mattress replacement or foam overlay? A prospective study on the incidence of pressure ulcers. Applied Nursing Research 1997;10(3):111‐20. - PubMed
Whitney 1984 {published data only}
-
- Whitney JD, Fellows BJ, Larson E. Do mattresses make a difference?. Journal of Gerontological Nursing 1984;10(9):20‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Allen 1993 {published data only}
-
- Allen V, Ryan DW, Murray A. Potential for bed sores due to high pressures: influence of body sites, body position, and mattress design. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1993;47(4):195‐7. - PubMed
Andrews 1989 {published data only}
-
- Andrews J, Balai R. The prevention and treatment of pressure sores by use of pressure distributing mattresses. Care Science and Practice 89;7(3):72‐6. - PubMed
Bales 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bales I. A comparison between the use of intravenous bags and the Heelift suspension boot to prevent pressure ulcers in orthopedic patients. Advances in Skin & Wound Care 2012;25(3):125‐131. - PubMed
Ballard 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ballard K. Pressure‐relief mattresses and patient comfort. Professional Nurse 1997;13(1):27‐32. - PubMed
Barhyte 1995 {published data only}
-
- Barhyte DY, McCance L, Valenta A, Tatenhove J, Walker MS, Bethea S. Selection of a standard hospital mattress: data‐based decision making. Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 1995;22(6):267‐70. - PubMed
Berthe 2007 {published data only}
-
- Berthe JV, Bustillo A, Melot C, Fontaine S. Does a foamy‐block mattress system prevent pressure sores? A prospective randomised clinical trial in 1729 patients. Acta Chirurgica Belgica 2007;107(2):155‐61. - PubMed
Black 2012 {published data only}
-
- Black J, Berke C, Urzendowski G. Pressure ulcer incidence and progression in critically ill subjects: Influence of low air loss mattress versus a powered air pressure redistribution mattress. Journal of Wound Ostomy & Continence Nursing 2012;39(3):267‐273. - PubMed
Bliss 1967 {published data only}
-
- Bliss MR, McLaren R, Exton‐Smith AN. Mattresses for preventing pressure sores in geriatric patients. Medical Bulletin of the Ministry of Health 1966; Vol. 25:238‐68. - PubMed
Bliss 1995 {published data only}
-
- Bliss MR. Preventing pressure sores in elderly patients ‐ a comparison of seven mattress overlays. Age and Ageing 1995;24:297‐302. - PubMed
-
- Bliss MR. Randomised controlled trial of seven pressure relieving mattress overlays for preventing pressure sores in elderly patients. Conference of the Tissue Viability Society; 1994; Harrogate, UK. 1994:5.
Braniff‐Matthews 1997 {published data only}
-
- Braniff‐Matthews C, Rhodes J. Prevention versus treatment: long term management of care. New Approaches to the Management of Chronic Wounds. 1997:27‐9.
Brienza 2001 {published data only}
-
- Brienza DM, Karg PE, Geyer MJ, Kelsey S, Trefler E. The relationship between pressure ulcer incidence and buttock‐seat cushion interface pressure in at‐risk elderly wheelchair users. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2001;82(4):529‐33. - PubMed
-
- Geyer MJ, Brienza D, Karg P, Kelsey S, Trefler E. Are commercial seat cushions efficacious in preventing pressure ulcers in the at‐risk, elderly nursing home population?. The 13th Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and 10th Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair. USA: HMP Communications, LLC, 2000.
Büchner 1995 {published data only}
-
- Büchner T. Comparison of 3 decubitus prevention measures stemming from the same principle ‐ with reference to cost‐benefit analysis. Krankenpflege 1995;33(6):248‐52. - PubMed
Cassino 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cassino R, Ippolito AM, Cuffaro C, Corsi A, Ricci E. A controlled, randomised study on the efficacy of two overlays in the treatment of decubitus ulcers. Minerva chirurgica 2013;68(1):105‐116. - PubMed
Chaloner 2000 {published data only}
-
- Chaloner D. A prospective, controlled comparison between two dynamic alternating mattress replacement systems within a community setting. 9th European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1999, 9‐11 November; Harrogate UK. 2000:9‐11.
Colin 1996 {published data only}
-
- Colin D, Loyant R, Abraham P, Saumet JL. Changes in sacral transcutaneous oxygen tension in the evaluation of different mattresses in the prevention of pressure ulcers. Advances in Wound Care 1996;9(1):25‐8. - PubMed
Conine 1991 {published data only}
-
- Conine TA, Hershler C. Effectiveness: a neglected dimension in the assessment of rehabilitation devices and equipment. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1991;14(2):117‐22. - PubMed
deBoisblanc 1993 {published data only}
-
- deBoisblanc BP, Castro M, Everret B, Grender J, Walker CD, Summer WR. Effect of air‐supported, continuous, postural oscillation on the risk of early ICU pneumonia in non‐traumatic clinical illness. Chest 1993;103(5):1543‐7. - PubMed
Defloor 1997 {published data only}
-
- Defloor T. The effect of position and mattress on the development of pressure sores. Verpleegkunde 1997;12(3):140‐9. - PubMed
Defloor 2000 {published data only}
-
- Defloor T. The effect of position and mattress on interface pressure. Applied Nursing Research 2000;13(1):2‐11. - PubMed
Defloor 2005 {published data only}
-
- Defloor T. Less frequent turning intervals and yet less pressure ulcers [Wisselhounding minder frequent en toch minder decubitus]. Tijdschrift voor Gerontologie en Geriatrie 2001;32:174‐7. - PubMed
-
- Defloor T, Bacquer D, Grypdonck MHF. The effect of various combinations of turning and pressure reducing devices on the incidence of pressure ulcers. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2005;42:37‐46. - PubMed
Della Valle 2001 {published data only}
-
- Della Valla AG, Salonia‐Ruzo P, Peterson MGE, Salvati EA, Sharrock NE. Inflatable pillows as axillary support devices during surgery performed in the lateral decubitus position under epidural anesthesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2001;93(5):1338‐43. - PubMed
Flam 1995 {published data only}
-
- Flam E, Isayeva E, Kipervas Y, Shklyarevsky V, Raab L. Skin temperature and moisture management with a low air loss surface. Ostomy Wound Management 1995;41(9):50‐6. - PubMed
Fleischer 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fleischer I, Bryant D. Evaluating replacement mattresses. Nurse Management 1997;28(8):38‐42. - PubMed
Geelkerken 1994 {published data only}
-
- Geelkerken RH, Breslau PJ, Hermans J, Wille J, Hofman A, Hamming JJ. Anti‐decubitus mattress (letter; comment). Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde 1994;138(36):1834. - PubMed
Gil Agudo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gil‐Agudo A, Peña‐González A, Ama‐Espinosa A, Pérez‐Rizo E, Díaz‐Domínguez E, Sánchez‐Ramos A. Comparative study of pressure distribution at the user‐cushion interface with different cushions in a population with spinal cord injury. Clinical Biomechanics 2009;24(7):558‐63. - PubMed
Gray 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gray D, Cooper P, Bertram M, Duguid K, Pirie G. A clinical audit of the Softform Premier Active[trademark] mattress in two acute care of the elderly wards. Wounds UK 2008;4(4):124‐8.
Grindley 1996 {published data only}
-
- Grindley A, Acres J. Alternating pressure mattresses: comfort and quality of sleep. British Journal of Nursing 1996;5(21):1303‐10. - PubMed
Grisell 2008 {published data only}
-
- Grisell M, Place HM. Face tissue pressure in prone positioning: a comparison of three face pillows while in the prone position for spinal surgery. Spine 2008;33(26):2938‐41. - PubMed
Gunningberg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Gunningberg L, Lindholm C, Carlsson M, Sjoden PO. Patients with hip fracture: risk for pressure ulcers. A prospective, controlled study of 124 patients in Uppsala, Sweden. European Wound Management Association and Journal of Wound Care Autumn Conference; 1998 November; Harrogate, UK. 1998:10.
Haalboom 1994 {published data only}
-
- Haalboom J R. Anti‐decubitus mattresses. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde 1994;138(26):1309‐10. - PubMed
Hampton 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hampton S. Can electric beds aid pressure sore prevention in hospitals?. British Journal of Nursing 1998;7(17):1010‐7. - PubMed
Hawkins 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hawkins JE. The effectiveness of pressure‐reducing table pads as an intervention to reduce the risk of intraoperatively acquired pressure sores. Military Medicine 1997;162:759‐61. - PubMed
Heyneman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Heyneman A, Vanderwee K, Grypdonck M, Defloor T. Effectiveness of two cushions in the prevention of heel pressure ulcers. Worldviews on Evidence‐Based Nursing 2009;6(2):114‐20. - PubMed
Holzgreve 1993 {published data only}
-
- Holzgreve A, Waldner M, Waldner PW, Hohlbach G. Bed sore prophylaxis in patients with chronic arterial occlusive disease with a new thermoactive pressure alternating mattress. Langenbecks Archiv fur Chirurgie 1993;Suppl Kongessbericht:1117.
Huang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Huang TT, Tseng CE, Lee TM, Yeh JY, Lai YY. Preventing pressure sores of the nasal ala after nasotracheal tube intubation: from animal model to clinical application. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2009;67(3):543‐51. - PubMed
Huang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Huang HY, Chen HL, Xu XJ. Pressure‐redistribution surfaces for prevention of surgery‐related pressure ulcers: A meta‐analysis. Ostomy/Wound Management 2013;59(4):36‐48. - PubMed
Inman 1999 {published data only}
-
- Inman KJ, Dymock K, Fysh N, Robbins B, Rutledge FS, Sibbald WJ. Pressure ulcer prevention: a randomized controlled trial of 2 risk‐directed strategies for patient surface assignment. Advances in Wound Care 1999;12(2):72‐80. - PubMed
Jacksich 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jacksich BB. Pressure ulcer prevalence and prevention of nosocomial development: one hospital's experience. Ostomy/Wound Management 1997;43(3):32‐4, 36, 38‐40. - PubMed
Jackson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jackson M, McKenney T, Drumm J, Merrick B, LeMaster T, VanGilder C. Pressure ulcer prevention in high‐risk postoperative cardiovascular patients. Critical Care Nurse 2011;31(4):44‐53. - PubMed
Jesurum 1996 {published data only}
-
- Jesurum J, Joseph K, Davis JM. Balloons, beds and breakdown. Effects of low air loss therapy on the development of pressure ulcers in cardiovascular surgical patients with intra‐aortic balloon pump support. Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America 1996;8(4):423‐40. - PubMed
Koo 1995 {published data only}
-
- Koo TK, Mak AF, Lee YL. Evaluation of an active seating system for pressure relief. Assistive Technology 1995;7(2):119‐28. - PubMed
Marchand 1993 {published data only}
-
- Marchand AC, Lidowski H. Reassessment of the use of genuine sheepskin for pressure ulcer prevention and treatment. Decubitus 1993;6(1):44‐7. - PubMed
McMichael 2008 {published data only}
-
- McMichael JC, Place HM. Face tissue pressures in prone positioning: a comparison of 3 pillows. Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques 2008;21(7):508‐13. - PubMed
Nakahara 2012 {published data only}
-
- Nakahara R, Ohto S, Kato H. Treating pressure ulcers using alternating pressure replacement mattresses. 4th congress of the world union of wound healing societies; september2‐6. Yokohama, Japan, 2012.
Neander 1996 {published data only}
-
- Neander KD, Michels S, Bering F, Rich A, Merseburg M. Effects of soft bedding on body perception and posture. Pflege 1996;9(4):293‐9. - PubMed
Ooka 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ooka M, Kemp MG, McMyn R, Shott S. Evaluation of three types of support surfaces for preventing pressure ulcers in patients in a surgical intensive care unit. Journal of Wound Ostomy Continence Nursing 1995;22(6):271‐9. - PubMed
Pham 2011a {published data only}
-
- Pham B, Stern A, Chen W, Sander B, John‐Baptiste A, Thein HH, Gomes T, Wodchis WP, Bayoumi A, Machado M, Carcone S, Krahn M. Preventing pressure ulcers in long‐term care: A cost‐effectiveness analysis. Archives of Internal Medicine 2011;171(20):1839‐47.. - PubMed
Pham 2011b {published data only}
-
- Pham B, Teague L, Mahoney J, Goodman L, Paulden M, Poss J, Li J, Ieraci L, Carcone S, Krahn M. Early prevention of pressure ulcers among elderly patients admitted through emergency departments: a cost‐effectiveness analysis. Annals of emergency medicine 2011;58(5):468‐478. e3. - PubMed
Phillips 1999 {published data only}
-
- Phillips L. Providing correct pressure‐relieving devices for optimum outcome. British Journal of Nursing 1999;8(21):1447‐52. - PubMed
Regan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Regan MB, Byers BH, Mayrovitz HN. Efficacy of a comprehensive pressure ulcer prevention programme in an extended care facility. Advances in Wound Care 1995;8(3):51‐5. - PubMed
Reynolds 1994 {published data only}
-
- Reynolds A, Suarez C. Pressure‐reducing capability of Conforma II mattress overlay. Advances in Wound Care 1994;7:36‐40. - PubMed
Rosenthal 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rosenthal MJ, Felton RM, Hileman DL, Lee M, Friedman M. A wheelchair cushion designed to redistribute sites of sitting pressure. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1996;77:278‐82. - PubMed
Scott 1995 {published data only}
-
- Scott F. Easing the pressure for hip fracture patients. Nursing Times 1995;91(29):30‐1. - PubMed
Scott 1999 {published data only}
-
- Scott EM, Baker EA, Kelly PJ, Stoddard EJ, Leaper DJ. Measurement of interface pressures in the evaluation of operating theatre mattresses. Journal of Wound Care 1999;8:437‐41. - PubMed
Scott 2000 {published data only}
-
- Scott EM. The prevention of pressure ulcers in the operating department. Journal of Wound Care 2000;9(1):18‐21. - PubMed
Simonis 2012 {published data only}
-
- Simonis G, Steiding K, Schaefer K, Rauwolf T, Strasser RH. A prospective, randomized trial of continuous lateral rotation (“kinetic therapy”) in patients with cardiogenic shock. Clinical Research in Cardiology 2012;101(12):955‐962. - PubMed
Stoneberg 1986 {published data only}
-
- Stoneberg C, Pitcock N, Myton C. Pressure sores in the homebound: one solution. American Journal of Nursing 1986;April:426‐8. - PubMed
Suarez 1995 {published data only}
-
- Suarez CH, Reynolds A. Pressure reduction with a hospitalized population using a mattress overlay. Ostomy Wound Management 1995;41:58‐60, 62‐3. - PubMed
Taccone 2009 {published data only}
-
- Taccone P, Polli F, Mietto C, Gattinoni L. Effects of a new rotational device on complication rate during prone ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective analysis. Intensive Care Medicine 2009;36(4):585‐99.
Takala 1994 {published data only}
-
- Takala J, Soini HO, Soppi E, Kataja M, Olkkonen K. Is it possible to reduce the risk factors of pressure sores by means of special mattresses?. Duodecim 1994;110(4):407‐14. - PubMed
Thomas 1994 {published data only}
-
- Thomas J. Support surface evaluation methodological and statistical considerations. Journal of Tissue Viability 1994;4(3):93.
Timmons 2008 {published data only}
-
- Timmons J, Bertram M. The use of micro‐stimulation in pressure ulcer prevention. Wounds UK 2008;4(4):120‐3.
Torra i Bou 2002 {published data only}
-
- Torra i Bou JE, Rueda López J, Camañes G, Herrero Narváez E, Blanco Blanco J, Martínez‐Esparza EH, et al. Heel pressure ulcers. Comparative study between heel protective bandage and hydrocellular dressing with special form for the heel. Revista de Enfermeria 2002;25(5):50‐6. - PubMed
Turnage‐Carrier 2008 {published data only}
-
- Turnage‐Carrier C, McLane KM, Gregurich MA. Interface pressure comparison of healthy premature infants with various neonatal surfaces. Advances in Neonatal Care 2008;8(3):176‐84. - PubMed
Vanderwee 2007 {published data only}
-
- Vanderwee K, Grypdonck MH, Bacquer D, Defloor T. Effectiveness of turning with unequal time intervals on the incidence of pressure ulcer lesions. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2007;57(1):59‐68. - PubMed
Vanderwee 2008 {published data only}
-
- Vanderwee K, Grypdonck M, Defloor T. Alternating pressure air mattresses as prevention for pressure ulcers: a literature review. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2008;45(5):784‐801. - PubMed
Wells 1984 {published data only}
-
- Wells P, Geden E. Paraplegic body‐support pressure on convoluted foam, waterbed, and standard mattresses. Research in Nursing and Health 1984;7(2):127‐33. - PubMed
Wild 1991 {published data only}
-
- Wild D. Body pressures and bed surfaces. Nursing Standard 1991;5(27):23, 25‐7. - PubMed
Wu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wu T, Wang ST, Lin PC, Liu CL, Chao YFC. Effects of using a high‐density foam pad versus a viscoelastic polymer pad on the incidence of pressure ulcer development during spinal surgery. Biological Research for Nursing 2011;13(4):419‐424. - PubMed
Zernike 1994 {published data only}
-
- Zernike W. Preventing heel pressure sores: a comparison of heel pressure relieving devices. Journal of Clinical Nursing 1994;3(6):375‐80. - PubMed
Zernike 1997 {published data only}
-
- Zernike W. Heel pressure relieving devices how effective are they?. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing 1997;14(4):12‐9. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Allegretti 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Allegretti A. Factors associated with clinical decisions and pressure ulcer development in long term care residents. University of Pittsburgh.
Mastrangelo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mastrangelo D, Farina E, Gallicchio V, Anna D, Bresadola F, FArina MA. Initial analyses of the prospective study randomized on the anti‐decubitis lesion mattress cover. SAWC Spring: The Symposium on Advanced Wounds Care and the Wound Healing Society; 2010, April 17‐20; Orlando, Florida. 2010:S32, Abstract CR‐053.
Mayer 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mayer H, Schröder G, Osterbrink J. Clinical evaluation of the efficiency of the micro‐stimulation‐system thevo‐activ: Final report [Klinische Evaluation der Wirksamkeit des MiS Micro‐Stimulations‐Systems Thevo‐Activ]. Florida International University 2008.
Rafter 2011 {published data only}
-
- Rafter L. Evaluation of patient outcomes: pressure ulcer prevention mattresses. British Journal of Nursing 2011;20(11):32. - PubMed
Additional references
Allman 1997
-
- Allman RM. Pressure ulcer prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and impact. Clinical Geriatric Medicine 1997;13(3):421‐36. - PubMed
Banks 1998
-
- Banks V. Nutrition and pressure area management. Journal of Wound Care 1998;7(6):318‐9. - PubMed
Benbow 1996
-
- Benbow M. Pressure sore guidelines: patient/carer involvement and education. British Journal of Nursing 1996;5(3):182,184‐7. - PubMed
Bennett 2004
-
- Bennett G, Dealey C, Posnett J. The cost of pressure ulcers in the UK. Age and Ageing 2004;33(3):230‐5. - PubMed
Bergstrom 1998
-
- Bergstrom, N, Braden, B, Champagne, M, Kemp, M, & Ruby, E. Predicting pressure ulcer risk: a multisite study of the predictive validity of the Braden Scale. Nursing Research 1998;47(5):261‐269. - PubMed
Berlowitz 1990
-
- Berlowitz DR, Wilikin SVB. Risk factors for pressure sores: a comparison of cross‐sectional and cohort derived data. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1990;37(11):1043‐50. - PubMed
Berlowitz 1997
-
- Berlowitz DR, Brandeis GH, Anderson J, Brand HK. Predictors of pressure ulcer healing among long‐term care residents. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1997;45(1):30‐4. - PubMed
Bianchetti 1993
-
- Bianchetti A, Zanetti O, Rozzini R, Trabucchi M. Risk factors for the development of pressure sores in hospitalized elderly patients: results of a prospective study. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 1993;16(3):225‐32. - PubMed
Bliss 1993
-
- Bliss MR, Thomas JM. Clinical trials with budgetary implications: establishing randomised trials of pressure‐relieving aids. Professional Nurse 1993;8(5):292‐6. - PubMed
Bo 2003
-
- Bo M, Massaia M, Raspo S, Bosco F, Cena P, Molaschi M, et al. Predictive factors of in‐hospital mortality in older patients admitted to a medical intensive care unit. Journal of American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(4):529‐33. - PubMed
Briggs 2013
Casey 1997
-
- Casey G. Nutrition helps wound healing. Nursing New Zealand 1997;3(11):19. - PubMed
Casey 1998
-
- Casey G. The importance of nutrition in wound healing. Nursing Standard 1998;13(3):51‐2. - PubMed
Choi 1992
-
- Choi SC, Nelson LD. Kinetic therapy in critically ill patients: combined results based on meta‐analysis. Journal of Critical Care 1992;7:57‐62.
Clough 1994
-
- Clough NP. The cost of pressure area management in an intensive care unit. Journal of Wound Care 1994;3:33‐5. - PubMed
Darouiche 1994
-
- Darouiche RO, Landon GC, Klima M, Musher DM, Markowski J. Osteomyelitis associated with pressure sores. Archives of Internal Medicine 1994;154(7):753‐8. - PubMed
Deeks 1998
Ek 1990
-
- Ek AC, Larsson J, Schenck H, Thorslund S, Unosson M, Bjurulf P. The correlation between energy, malnutrition and clinical outcome in an elderly hospital population. Clinical Nutrition 1990;9(4):185‐9. - PubMed
Elliot 1999
-
- Elliott TR, Shewchuk RM, Scott Richards J. Caregiver social problem‐solving abilities and family member adjustment to recent‐onset physical disabilities. Rehabilitation Psychology 1999;44(1):104‐23.
Emflorgo 1999
-
- Emflorgo CA. The assessment and treatment of wound pain. Journal of Wound Care 1999;8(8):384‐5. - PubMed
EPUAP‐NPUAP 2009
-
- European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel and National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel. Prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers: quick reference guide. Washington DC: National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel 2009.
Flock 2003
-
- Flock P. Pilot study to determine the effectiveness of diamorphine gel to control pressure ulcer pain. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2003;25(6):547‐54. - PubMed
Franks 1999
-
- Franks PJ, Morfatt CJ. Focus on wound management: Quality of life issue in chronic wound management. British Journal of Community Nursing 1999;4(6):283‐4.
Franks 2002
-
- Franks PJ, Winterburg JH, Moffatt CJ. Health‐related quality of life and pressure ulceration assessment in patients treated in the community. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2002;10(3):133‐40. - PubMed
Freeman 2001
-
- Freeman K, Smyth C, Dallam L, Jackson B. Pain measurement scales: a comparison of the visual analogue and faces rating scales in measuring pressure ulcer pain (comment). Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2001;28(6):290‐6. - PubMed
Gallagher 1997
-
- Gallagher SM. Morbid obesity: a chronic disease with an impact on wound and related problems. Ostomy/Wound Management 1997;43(5):18‐24,26‐7. - PubMed
Gosnell 1973
-
- Gosnell DJ. An assessment tool to identify pressure sores. Nursing Research 1973;22:55‐59. - PubMed
Graves 2005
-
- Graves N, Birrell F, Whitby M. Effect of pressure ulcers on length of hospital stay. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 2005;26(3):293‐7. - PubMed
Hagelstein 1995
-
- Hagelstein SM, Banks V. Maintaining quality of life for elderly patients in residential care. Journal of Wound Care 1995;8(4):347‐8. - PubMed
Healy 2003
-
- Healy M. Wound care and pain. World of Irish Nursing 2003;11(5):39‐40.
Hefley 1990
-
- Hefley ML, Radcliffe J. The 1988‐1989 decubitus study. Can a standardization of treatment be set for the elderly patient with decubiti ulcers stage III?. Hawaii Medical Journal 1999;49(9):346, 349‐50. - PubMed
Henoch 2003
-
- Henoch I, Gustafsson M. Pressure ulcers in palliative care:development of a hospice pressure ulcer risk assessment scale. International Journal of Palliative Nursing 2003 2003;9(11):474–84. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Junkin 2009
-
- Junkin J, Gray M. Are pressure redistribution surfaces or heel protection devices effective for preventing heel pressure ulcers?. Journal of Wound Ostomy Continence Nursing 2009;36(6):602‐8. - PubMed
Kaltenhalter 2001
-
- Kaltenhaler E, Whitfield, Walters SJ, Akehurst RL, Paisley S. UK, USA and Canada: how do their pressure ulcer prevalence and incidence data compare?. Journal of Wound Care 2001;10(1):530‐5. - PubMed
Krainski 1992
-
- Krainski MM. Pressure ulcers and the elderly. Ostomy Wound Management 1992;38(5):22. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2009
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Livesley 2002
-
- Livesley NJ, Chow AW. Infected pressure ulcers in elderly individuals. Clinical infectious diseases 2002;35:1390–6. - PubMed
Manfredi 2002
-
- Manfredi PL, Breuer B, Meier DE, Libow L. Pain assessment in the elderly with severe dementia. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2002;25(1):48‐52. - PubMed
McInnes 2011
-
- McInnes E, Dumville JC, Jammali‐Blasi A, Bell‐Syer SEM. Support surfaces for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue Issue 12. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. CONSORT group. JAMA 2001;285(15):1987‐91. - PubMed
Norton 1979
-
- Norton D, McLaren R, Exton‐Smith A.N. An Investigation of Geriatric Problems in Hospital. 3rd Edition. London: Churchill Livingstone, 1979.
NPUAP 2007
-
- National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP). Support Surface Standards Initiative. Terms and Definitions Related to Support Surfaces. www.npuap.org/NPUAP_S3I_TD.pdf 2007.
NPUAP‐EPUAP‐PPPIA 2014
-
- National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel and Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance. International NPUAP/EPUAP pressure ulcer classification system. In: Emily Haesler editor(s). Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers: Quick Reference Guide. Perth, Australia: Cambridge Media, 2014:11‐13.
Orlando 1998
-
- Orlando PL. Pressure ulcer management in the geriatric patient. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 1998;32(11):1221‐7. - PubMed
Pase 1998
-
- Pase MN, Hoffman RG. Selection and use of risk assessment tools and treatment protocol in extended care facilities in the southwest. Journal of Wound Ostomy and Continence Nursing 1998;25(1):44‐50. - PubMed
Phillips 2009
-
- Phillips L, Buttery J. Exploring pressure ulcer prevalence and preventative care. Nursing Times 2009;105(16):34‐6. - PubMed
Prior 2002
-
- Prior J. The pressure is on: midwives and decubitus ulcers. RCM Midwives Journal 2002;5(5):196‐200. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014. Review Manager (RevMan). The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014, Version 5.3.
Ronda 2002
-
- Ronda L, Falce RL. Skin care in older people. Primary Health Care 2002;12(7):51‐7.
SIGN 2008
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Search filters. http://www.sign.ac.uk/methodology/filters.html#random (accessed 28 February 2008).
Spoelhof 2000
-
- Spoelhof GD. Management of pressure ulcers in the nursing home. Annals of Long Term Care 2000;8(8):69‐77.
Thomas 1996
-
- Thomas DR, Goode PS, Tarquine PH, Allman RM. Hospital acquired pressure ulcers and risk of death. Journal of American Geriatrics Society 1996;44:1435‐40. - PubMed
Thomas 2001
-
- Thomas DR. Improving outcomes of pressure ulcers with nutritional interventions: a review of the evidence. Nutrition 2001;17:121‐5. - PubMed
Vanderwee 2007a
-
- Vanderwee K, Clark M, Dealey C, Gunningberg L, Defloor T. Pressure ulcer prevalence in Europe: a pilot study. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 2007;13(2):227‐35. - PubMed
VanGilder 2009
-
- VanGilder C, Amlung S, Harrison P, Meyer S. Results of the 2008‐2009 International Pressure Ulcer Prevalence Survey and a 3‐year, acute care, unit‐specific analysis. Ostomy/Wound Management 2009;55(11):39‐45. - PubMed
Waltman 1991
-
- Waltman NL, Bergstrom N, Armstrong N, Norvell K, Braden B. Nutritional status, pressure sores, and mortality in elderly patients with cancer. Oncology Nursing Forum 1991;18(5):867‐73. - PubMed
Waterlow 1985
-
- Waterlow J. A risk assessment card. Nursing Times 1985;81(49):51‐5. - PubMed
Whittington 2004
-
- Whittington K, Briones R. National prevalence and incidence study: 6‐year sequential acute care data. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2004;17(9):490‐5. - PubMed
Woodbury 2004
-
- Woodbury M, Houghton P. Prevalence of pressure ulcers in Canadian healthcare settings. Ostomy/Wound Management 2004;50(10):22‐4,26,28,30,32,34,36‐8. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Cullum 1995
Cullum 2001
-
- Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, Sheldon T. Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) Beds: (6) Compression: (7) Laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy. Health Technology Assessment 2001;5(9):1‐221. - PubMed
Cullum 2003
-
- Cullum N, Nelson EA, Nixon JE. Pressure Sores. Clinical Evidence. Vol. 9, London: BMJ Publishing Group, June 2003:408‐9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

