Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis to chickpea in a 17-year-old female: a case report
- PMID: 26334308
- PMCID: PMC4559180
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-015-0669-6
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis to chickpea in a 17-year-old female: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis is a subtype of anaphylaxis and, although rare, it is an important condition to be familiar with as it can ultimately lead to death.
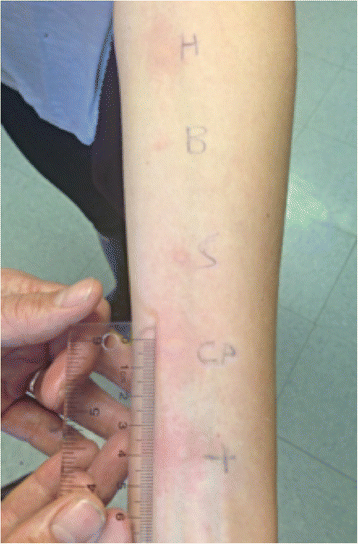
Case presentation: We present a case of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in a 17-year-old white girl due to chickpea. She had a history of anaphylaxis after eating crackers and hummus before exercising. Skin prick testing and serum-specific immunoglobulin E level confirmed chickpea to be the causative allergen.
Conclusions: This case demonstrates the challenge in identifying specific causative food allergens when foods are eaten in combination, when the food is processed, and when cross-reactivity is possible. These challenges add complexity to a condition that is already rare and unfamiliar to some health care providers. We hope that this case will serve as an important reminder that although rare, food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis exists and making a diagnosis can lead to life-saving preventative strategies. As legumes are not a common food associated with food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis, this will add to our current knowledge base in the field of allergy.
Figures
References
-
- Sampson HA, Munoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, Adkinson NF, Jr, Bock SA, Branum A, et al. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report – Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network Symposium. Ann Emerg Med. 2006;47:373–80. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.01.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials