Loss of miR-200b promotes invasion via activating the Kindlin-2/integrin β1/AKT pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: An E-cadherin-independent mechanism
- PMID: 26334393
- PMCID: PMC4745703
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5027
Loss of miR-200b promotes invasion via activating the Kindlin-2/integrin β1/AKT pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: An E-cadherin-independent mechanism
Abstract
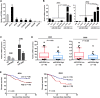
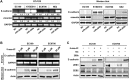
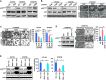
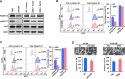
Our previous studies have shown that loss of miR-200b enhances the invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells. However, whether the miR-200-ZEB1/2-E-cadherin regulatory cascade, a master regulator of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), is involved in the regulation of ESCC invasion remains elusive. Here, we show that miR-200b represses ESCC cell invasion in vivo without altering the expression of E-cadherin and vimentin, two surrogate markers of EMT. However, an inverse correlation was observed between the expression levels of miR-200b and ZEB1/2 in both ESCC cell lines (n = 7, P < 0.05) and ESCC tumor samples (n = 88, P < 0.05). Methylation of E-cadherin gene was found to block the regulation of E-cadherin by the miR-200b-ZEB1/2 axis, indicating that an E-cadherin-independent mechanism can mediate the biological function of miR-200b in ESCC. We revealed that miR-200b suppresses the integrin β1-AKT pathway via targeting Kindlin-2 to mitigate ESCC cell invasiveness. In two independent cohorts of ESCC samples (n = 20 and n = 53, respectively), Kindlin-2 expression positively correlated with the activation status of both the integrin signaling pathway and the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway (both P < 0.01). These data highlight that suppression of the Kindlin-2-integrin β1-AKT regulatory axis is an alternative mechanism underlying the tumor suppressor function of miR-200b in ESCC.
Keywords: E-cadherin; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; invasion; miR-200; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-150 is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting the EMT inducer ZEB1.Cancer Sci. 2013 Jan;104(1):48-54. doi: 10.1111/cas.12030. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23013135 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200b suppresses invasiveness and modulates the cytoskeletal and adhesive machinery in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting Kindlin-2.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Feb;35(2):292-301. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt320. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24064224
-
Long non-coding RNA ATB promotes malignancy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-200b/Kindlin-2 axis.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 22;8(6):e2888. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.245. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28640252 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between E-cadherin and microRNA deregulation in head and neck cancers: the potential interplay.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:126038. doi: 10.1155/2014/126038. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25161999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancers; focusing on mir-200 family.Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2021;28:100385. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100385. Epub 2021 May 11. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 34023767 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in squamous cell carcinoma with an especial focus on head and neck cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Aug 13;22(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02676-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35964082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway related microRNAs in esophageal cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Mar 26;10(9):2678-2686. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2678. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35434118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β1 Integrins as Therapeutic Targets to Disrupt Hallmarks of Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 24;6:279. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00279. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26635609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA CCAT2 Promotes the Development of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inhibiting miR-200b to Upregulate the IGF2BP2/TK1 Axis.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 27;11:680642. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.680642. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34386421 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the microRNA-200 Family, microRNA-205, and Markers of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition as Predictors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection over Esophagectomy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Single-Center Experience.Cells. 2020 Feb 20;9(2):486. doi: 10.3390/cells9020486. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32093260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–9217. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–2252. - PubMed
-
- McCann J. Esophageal Cancers: Changing Character, Increasing Incidence. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999;91:497–498. - PubMed
-
- Ries LAG, Eisner MP, Kosary CL. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1973-1999. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

