Epigenetic silencing of NTSR1 is associated with lateral and noninvasive growth of colorectal tumors
- PMID: 26334593
- PMCID: PMC4745776
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5034
Epigenetic silencing of NTSR1 is associated with lateral and noninvasive growth of colorectal tumors
Abstract
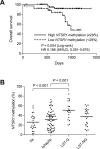
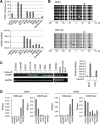
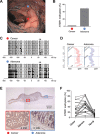
Our aim was to identify DNA methylation changes associated with the growth pattern and invasiveness of colorectal cancers (CRCs). Comparison of the methylation statuses of large (≥ 20 mm in diameter along the colonic surface) noninvasive tumors (NTs) and small (<20 mm in diameter along the colonic surface) invasive tumors (ITs) using CpG island microarray analysis showed neurotensin receptor 1 (NTSR1) to be hypermethylated in large NTs. Quantitative bisulfite pyrosequencing revealed that NTSR1 is frequently methylated in colorectal tumors, with large NTs exhibiting the highest methylation levels. The higher NTSR1 methylation levels were associated with better prognoses. By contrast, NTSR1 copy number gains were most frequent among small ITs. Methylation of NTSR1 was associated with the gene's silencing in CRC cell lines, whereas ectopic expression of NTSR1 promoted proliferation and invasion by CRC cells. Analysis of primary tumors composed of adenomatous and malignant portions revealed that NTSR1 is frequently methylated in the adenomatous portion, while methylation levels are generally lower in the cancerous portions. These results suggest that NTSR1 methylation is associated with lateral and noninvasive growth of colorectal tumors, while low levels of methylation may contribute to the malignant potential through activation of NTSR1. Our data also indicate that NTSR1 methylation may be a prognostic biomarker in CRC.
Keywords: DNA methylation; LST; biomarker; colorectal tumor; invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neurotensin pathway in digestive cancers and clinical applications: an overview.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Dec 2;11(12):1027. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03245-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33268796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse expression patterns and tumorigenic role of neurotensin signaling components in colorectal cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jun;50(6):2200-2206. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3990. Epub 2017 May 9. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28498396 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression and tumorigenic function of neurotensin receptor 1 in neuroendocrine tumor cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):26960-70. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4745. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26298774 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotensin promotes the progression of malignant glioma through NTSR1 and impacts the prognosis of glioma patients.Mol Cancer. 2015 Feb 3;14:21. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0290-8. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25644759 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation patterns as noninvasive biomarkers and targets of epigenetic therapies in colorectal cancer.Epigenomics. 2016 May;8(5):685-703. doi: 10.2217/epi-2015-0013. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Epigenomics. 2016. PMID: 27102979 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotensin pathway in digestive cancers and clinical applications: an overview.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Dec 2;11(12):1027. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03245-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33268796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface microstructures are associated with mutational intratumoral heterogeneity in colorectal tumors.J Gastroenterol. 2018 Dec;53(12):1241-1252. doi: 10.1007/s00535-018-1481-z. Epub 2018 Jun 11. J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29948303
-
A Review of the Role of Neurotensin and Its Receptors in Colorectal Cancer.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017;2017:6456257. doi: 10.1155/2017/6456257. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 28316623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics Identified 17 Immune Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers for Breast Cancer: Application Study Based on Artificial Intelligence Algorithms.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 31;10:330. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00330. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32296631 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotensin receptors regulate transactivation of the EGFR and HER2 in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 15;865:172735. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172735. Epub 2019 Oct 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31614143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suzuki H, Tokino T, Shinomura Y, Imai K, Toyota M. DNA methylation and cancer pathways in gastrointestinal tumors. Pharmacogenomics. 2008;9:1917–1928. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto E, Suzuki H, Yamano HO, Maruyama R, Nojima M, Kamimae S, Sawada T, Ashida M, Yoshikawa K, Kimura T, Takagi R, Harada T, Suzuki R, et al. Molecular dissection of premalignant colorectal lesions reveals early onset of the CpG island methylator phenotype. Am J Pathol. 2012;181:1847–1861. - PubMed
-
- Yagi K, Takahashi H, Akagi K, Matsusaka K, Seto Y, Aburatani H, Nakajima A, Kaneda A. Intermediate methylation epigenotype and its correlation to KRAS mutation in conventional colorectal adenoma. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:616–625. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki H, Yamamoto E, Maruyama R, Niinuma T, Kai M. Biological significance of the CpG island methylator phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;455:35–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

