Expression of Lipid Metabolism-Related Proteins in Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26334757
- PMCID: PMC4559312
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137204
Expression of Lipid Metabolism-Related Proteins in Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The tumor biology of metastatic breast cancers differ according to the metastatic sites, and the features of cancer metabolism may also be different. The aim of this study is to investigate the expression of lipid metabolism-related proteins in metastatic breast cancer according to metastatic site and discuss the clinical significance thereof.
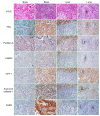
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining for lipid metabolism-related proteins [fatty acid synthase (FASN), hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), carnitine palmitoyltransferase IA (CPT-1A), acyl-CoA oxidase 1 (ACOX1), fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4,) and perilipin 1 (PLIN1)] was performed using a tissue microarray of 149 cases of metastatic breast cancer (bone metastasis = 39, brain metastasis = 37, liver metastasis = 21, and lung metastasis = 52).
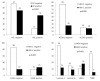
Results: The expression levels of ACOX1 (p = 0.009) and FASN (p = 0.007) varied significantly according to metastatic site, with the highest expression in brain metastasis and the lowest expression in liver metastasis. ACOX1 positivity (p = 0.005) and FASN positivity (p = 0.003) correlated with HER-2 positivity. The expression of FASN was significantly higher in HER-2 type breast cancer, and lower in luminal A and TNBC type breast cancer (p<0.001). Among lipid metabolism-related proteins, PLIN1 positivity was found to be an independent poor prognostic factor on multivariate analysis (Hazard ratio: 4.979, 95% CI: 1.054-22.59, p = 0.043).
Conclusion: Different expression levels of lipid metabolism-related proteins were observed according to metastatic site. The expression of ACOX1 and FASN was highest in brain metastasis. These results suggest that the metastatic site should be considered when using lipid metabolism inhibitors for targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential expression of lipid metabolism-related proteins in different breast cancer subtypes.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 9;10(3):e0119473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119473. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25751270 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of lipid metabolism-related proteins in breast phyllodes tumors.Neoplasma. 2016;63(2):254-62. doi: 10.4149/211_150715N393. Neoplasma. 2016. PMID: 26774147
-
Expression of Lipid Metabolism-Related Proteins Differs between Invasive Lobular Carcinoma and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 23;18(1):232. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010232. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28124996 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-linked HER2 expression: association with obesity and lipid-related microenvironment.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017 Oct 31;32(3):/j/hmbci.2017.32.issue-3/hmbci-2017-0020/hmbci-2017-0020.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2017-0020. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017. PMID: 29087955 Review.
-
Fatty acid synthase: a druggable driver of breast cancer brain metastasis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022 May;26(5):427-444. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2022.2077189. Epub 2022 May 19. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022. PMID: 35545806 Review.
Cited by
-
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) signalome: A molecular guide for precision oncology.Mol Oncol. 2024 Mar;18(3):479-516. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13582. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38158755 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate models from RNA-Seq SNVs yield candidate molecular targets for biomarker discovery: SNV-DA.BMC Genomics. 2016 Mar 31;17:263. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2542-4. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27029813 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Gynaecological Cancers: Is There a Role for Oestradiol?Metabolites. 2022 Apr 14;12(4):350. doi: 10.3390/metabo12040350. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35448537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for clinical axillary lymph node metastasis in T1-2 breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 13;12(1):687. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04495-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35027588 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiling of triple-negative breast cancer cells reveals metabolic vulnerabilities.Cancer Metab. 2017 Aug 22;5:6. doi: 10.1186/s40170-017-0168-x. eCollection 2017. Cancer Metab. 2017. PMID: 28852500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abali H, Celik I. High incidence of central nervous system involvement in patients with breast cancer treated with epirubicin and docetaxel. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002;25(6):632–3. Epub 2002/12/13. . - PubMed
-
- Colleoni M, O'Neill A, Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, on M, Thurlimann B, et al. Identifying breast cancer patients at high risk for bone metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(23):3925–35. Epub 2000/12/01. . - PubMed
-
- Evans AJ, James JJ, Cornford EJ, Chan SY, Burrell HC, Pinder SE, et al. Brain metastases from breast cancer: identification of a high-risk group. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2004;16(5):345–9. Epub 2004/09/03. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

