Carbapenem-resistant and carbapenem-susceptible isogenic isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 causing infection in a tertiary hospital
- PMID: 26335352
- PMCID: PMC4559076
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-015-0510-9
Carbapenem-resistant and carbapenem-susceptible isogenic isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 causing infection in a tertiary hospital
Abstract
Background: In this study we describe the clinical and molecular characteristics of an outbreak due to carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CR-KP) producing CTX-M-15 and OXA-48 carbapenemase. Isogenic strains, carbapenem-susceptible K. pneumoniae (CS-KP) producing CTX-M-15, were also involved in the outbreak.
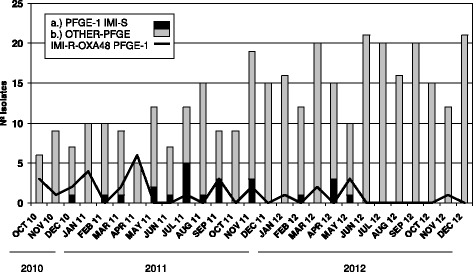
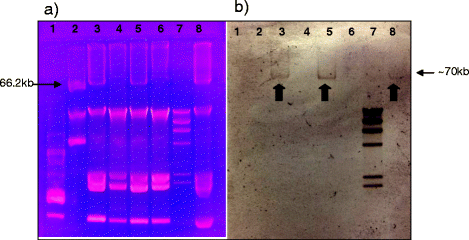
Results: From October 2010 to December 2012 a total of 62 CR-KP and 23 CS-KP were isolated from clinical samples of 42 patients (22 had resistant isolates, 14 had susceptible isolates, and 6 had both CR and CS isolates). All patients had underlying diseases and 17 of them (14 patients with CR-KP and 3 with CS-KP) had received carbapenems previously. The range of carbapenem MICs for total isolates were: imipenem: 2 to >32 μg/ml vs. <2 μg/ml; meropenem: 4 to >32 μg/ml vs. <2 μg/ml; and ertapenem: 8 to >32 μg/ml vs. <2 μg/ml. All the isolates were also resistant to gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, and cotrimoxazole. Both types of isolates shared a common PFGE pattern associated with the multilocus sequence type 101 (ST101). The bla CTX-M-15 gene was detected in all the isolates, whereas the bla OXA-48 gene was only detected in CR-KP isolates on a 70 kb plasmid.
Conclusions: The clonal spread of K. pneumoniae ST101 expressing the OXA-48 and CTX-M-15 beta-lactamases was the cause of an outbreak of CR-KP infections. CTX-M-15-producing isolates lacking the bla OXA-48 gene coexisted during the outbreak.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Two-Year Surveillance in Five Colombian Tertiary Care Hospitals Reveals High Frequency of Non-CG258 Clones of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with Distinct Clinical Characteristics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Oct 26;60(1):332-42. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01775-15. Print 2016 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26503660 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and the novel carbapenemases OXA-244 and OXA-245 in Spain.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Feb;68(2):317-21. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks383. Epub 2012 Oct 2. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23034714
-
Prevalence of a New Variant OXA-204 and OXA-48 Carbapenemases Plasmids Encoded in Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates in Tunisia.Microb Drug Resist. 2018 Mar;24(2):142-149. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2016.0236. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Microb Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 28737463
-
Long-lasting outbreak due to CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST336 in a rehabilitation ward: report and literature review.J Hosp Infect. 2017 Sep;97(1):42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Apr 9. J Hosp Infect. 2017. PMID: 28454769 Review.
-
Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: molecular and genetic decoding.Trends Microbiol. 2014 Dec;22(12):686-96. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Trends Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25304194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global Dissemination of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Genetic Context, Treatment Options, and Detection Methods.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jun 13;7:895. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00895. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27379038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OXA-48-like carbapenemases producing Enterobacteriaceae in different niches.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Apr;37(4):587-604. doi: 10.1007/s10096-017-3112-7. Epub 2017 Oct 8. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 28990132 Review.
-
Modelling of the transmission dynamics of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in hospitals and design of control strategies.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 9;12(1):3805. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07728-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35264643 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of carbapenem resistance on mortality in patients infected with Enterobacteriaceae: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2021 Dec 14;11(12):e054971. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-054971. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34907071 Free PMC article.
-
Dissemination of OXA-48- and NDM-1-Producing Enterobacterales Isolates in an Algerian Hospital.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 31;11(6):750. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11060750. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740155 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

