The dual role of iNOS in cancer
- PMID: 26335399
- PMCID: PMC4565017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.009
The dual role of iNOS in cancer
Abstract
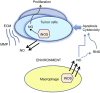
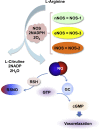
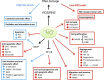
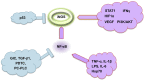
Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the 10 smallest molecules found in nature. It is a simple gaseous free radical whose predominant functions is that of a messenger through cGMP. In mammals, NO is synthesized by the enzyme nitric oxide synthase (NOS) of which there are three isoforms. Neuronal (nNOS, NOS1) and endothelial (eNOS, NOS3) are constitutive calcium-dependent forms of the enzyme that regulate neural and vascular function respectively. The third isoform (iNOS, NOS2), is calcium-independent and is inducible. In many tumors, iNOS expression is high, however, the role of iNOS during tumor development is very complex and quite perplexing, with both promoting and inhibiting actions having been described. This review will aim to summarize the dual actions of iNOS-derived NO showing that the microenvironment of the tumor is a contributing factor to these observations and ultimately to cellular outcomes.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cancer; Cell situation; Nitric oxide; Stroma; iNOS.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ignarro L.J., Napoli C., Loscalzo J. Nitric oxide donors and cardiovascular agents modulating the bioactivity of nitric oxide: an overview. Circ. Res. 2002;90:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Geller D.A., Billiar T.R. Molecular biology of nitric oxide synthases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1998;17:7–23. - PubMed
-
- Quinn A.C., Petros A.J., Vallance P. Nitric oxide: an endogenous gas. Br. J. Anaesth. 1995;74:443–451. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:907–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

