Appoptosin-Mediated Caspase Cleavage of Tau Contributes to Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Pathogenesis
- PMID: 26335643
- PMCID: PMC4575284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.08.020
Appoptosin-Mediated Caspase Cleavage of Tau Contributes to Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Pathogenesis
Erratum in
-
Appoptosin-Mediated Caspase Cleavage of Tau Contributes to Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Pathogenesis.Neuron. 2024 Dec 4;112(23):3984-3985. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.11.001. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 39520984 No abstract available.
Abstract
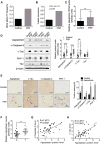
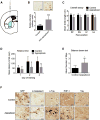
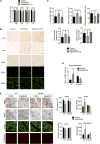
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a movement disorder characterized by tau neuropathology where the underlying mechanism is unknown. An SNP (rs1768208 C/T) has been identified as a strong risk factor for PSP. Here, we identified a much higher T-allele occurrence and increased levels of the pro-apoptotic protein appoptosin in PSP patients. Elevations in appoptosin correlate with activated caspase-3 and caspase-cleaved tau levels. Appoptosin overexpression increased caspase-mediated tau cleavage, tau aggregation, and synaptic dysfunction, whereas appoptosin deficiency reduced tau cleavage and aggregation. Appoptosin transduction impaired multiple motor functions and exacerbated neuropathology in tau-transgenic mice in a manner dependent on caspase-3 and tau. Increased appoptosin and caspase-3-cleaved tau were also observed in brain samples of patients with Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia with tau inclusions. Our findings reveal a novel role for appoptosin in neurological disorders with tau neuropathology, linking caspase-3-mediated tau cleavage to synaptic dysfunction and behavioral/motor defects.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Baker M, Litvan I, Houlden H, Adamson J, Dickson D, Perez-Tur J, Hardy J, Lynch T, Bigio E, Hutton M. Association of an extended haplotype in the tau gene with progressive supranuclear palsy. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:711–715. - PubMed
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nature Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Borroni B, Agosti C, Magnani E, Di Luca M, Padovani A. Genetic bases of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: the MAPT tau disease. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18:2655–2660. - PubMed
-
- Conrad C, Andreadis A, Trojanowski JQ, Dickson DW, Kang D, Chen X, Wiederholt W, Hansen L, Masliah E, Thal LJ, et al. Genetic evidence for the involvement of tau in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol. 1997;41:277–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG035355/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG11385/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG011385/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG021173/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021173/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044420/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 089703/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01NS046673/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG18440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- PN2 EY016525/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046673/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS076411/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 081864/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01NS66072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- PN1 EY016525/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG038710/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG5131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS076411/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG038710/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS074969/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027924/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS066072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG046205/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_G1000734/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01AG044420/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

