Distinct Subpopulations of Nucleus Accumbens Dynorphin Neurons Drive Aversion and Reward
- PMID: 26335648
- PMCID: PMC4625385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.08.019
Distinct Subpopulations of Nucleus Accumbens Dynorphin Neurons Drive Aversion and Reward
Abstract
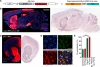
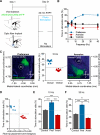
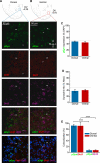
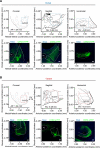
The nucleus accumbens (NAc) and the dynorphinergic system are widely implicated in motivated behaviors. Prior studies have shown that activation of the dynorphin-kappa opioid receptor (KOR) system leads to aversive, dysphoria-like behavior. However, the endogenous sources of dynorphin in these circuits remain unknown. We investigated whether dynorphinergic neuronal firing in the NAc is sufficient to induce aversive behaviors. We found that photostimulation of dynorphinergic cells in the ventral NAc shell elicits robust conditioned and real-time aversive behavior via KOR activation, and in contrast, photostimulation of dorsal NAc shell dynorphin cells induced a KOR-mediated place preference and was positively reinforcing. These results show previously unknown discrete subregions of dynorphin-containing cells in the NAc shell that selectively drive opposing behaviors. Understanding the discrete regional specificity by which NAc dynorphinerigic cells regulate preference and aversion provides insight into motivated behaviors that are dysregulated in stress, reward, and psychiatric disease.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Baldo BA, Daniel RA, Berridge CW, Kelley AE. Overlapping distributions of orexin/hypocretin- and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase immuno-reactive fibers in rat brain regions mediating arousal, motivation, and stress. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003;464:220–237. - PubMed
-
- Bals-Kubik R, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Evidence that the aversive effects of opioid antagonists and kappa-agonists are centrally mediated. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1989;98:203–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DA038725/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071051/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH101956/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK089044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK071051/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075632/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA033396/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK053477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA011605/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- TR01NS081707/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS081707/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027552/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DA038725/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK096010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DA038725/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA037152/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37DK053477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR027552/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA037152/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK075632/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

