HDL and CER-001 Inverse-Dose Dependent Inhibition of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in apoE-/- Mice: Evidence of ABCA1 Down-Regulation
- PMID: 26335690
- PMCID: PMC4559410
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137584
HDL and CER-001 Inverse-Dose Dependent Inhibition of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in apoE-/- Mice: Evidence of ABCA1 Down-Regulation
Abstract
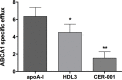
Objective: CER-001 is a novel engineered HDL-mimetic comprised of recombinant human apoA-I and charged phospholipids that was designed to mimic the beneficial properties of nascent pre-ß HDL. In this study, we have evaluated the dose-dependent regulation of ABCA1 expression in vitro and in vivo in the presence of CER-001 and native HDL (HDL3).
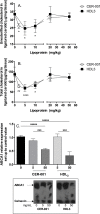
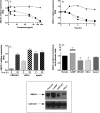
Methods and results: CER-001 induced cholesterol efflux from J774 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner similar to natural HDL. A strong down-regulation of the ATP-binding cassette A1 (ABCA1) transporter mRNA (- 50%) as well as the ABCA1 membrane protein expression (- 50%) was observed at higher doses of CER-001 and HDL3 compared to non-lipidated apoA-I. In vivo, in an apoE-/- mouse "flow cessation model," in which the left carotid artery was ligatured to induce local inflammation, the inhibition of atherosclerotic plaque burden progression in response to a dose-range of every-other-day CER-001 or HDL in the presence of a high-fat diet for two weeks was assessed. We observed a U-shaped dose-response curve: inhibition of the plaque total cholesterol content increased with increasing doses of CER-001 or HDL3 up to a maximum inhibition (- 51%) at 5 mg/kg; however, as the dose was increased above this threshold, a progressively less pronounced inhibition of progression was observed, reaching a complete absence of inhibition of progression at doses of 20 mg/kg and over. ABCA1 protein expression in the same atherosclerotic plaque was decreased by-45% and-68% at 50 mg/kg for CER-001 and HDL respectively. Conversely, a-12% and 0% decrease in ABCA1 protein expression was observed at the 5 mg/kg dose for CER-001 and HDL respectively.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate that high doses of HDL and CER-001 are less effective at slowing progression of atherosclerotic plaque in apoE-/- mice compared to lower doses, following a U-shaped dose-response curve. A potential mechanism for this phenomenon is supported by the observation that high doses of HDL and CER-001 induce a rapid and strong down-regulation of ABCA1 both in vitro and in vivo. In conclusion, maximally efficient HDL- or CER-001-mediated cholesterol removal from atherosclerotic plaque is achieved by maximizing macrophage-mediated efflux from the plaque while minimizing dose-dependent down-regulation of ABCA1 expression. These observations may help define the optimal dose of HDL mimetics for testing in clinical trials of atherosclerotic burden regression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
CER-001, a HDL-mimetic, stimulates the reverse lipid transport and atherosclerosis regression in high cholesterol diet-fed LDL-receptor deficient mice.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Jan;232(1):110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.10.018. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 24401224
-
Retinoic acid induces macrophage cholesterol efflux and inhibits atherosclerotic plaque formation in apoE-deficient mice.Br J Nutr. 2015 Aug 28;114(4):509-18. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515002159. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Br J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26201974
-
Novel formulation of a reconstituted high-density lipoprotein (CSL112) dramatically enhances ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Sep;33(9):2202-11. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301981. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23868939
-
High-Density Lipoprotein Mimetics: a Therapeutic Tool for Atherosclerotic Diseases.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016;23(4):385-94. doi: 10.5551/jat.33720. Epub 2016 Feb 1. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016. PMID: 26830201 Review.
-
HDL Mimetics Infusion and Regression of Atherosclerosis: Is It Still Considered a Valid Therapeutic Option?Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018 Jun 21;20(8):66. doi: 10.1007/s11886-018-1004-9. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29926215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthetic High-Density Lipoprotein-Mediated Targeted Delivery of Liver X Receptors Agonist Promotes Atherosclerosis Regression.EBioMedicine. 2018 Feb;28:225-233. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.12.021. Epub 2017 Dec 20. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 29361501 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol Efflux Efficiency of Reconstituted HDL Is Affected by Nanoparticle Lipid Composition.Biomedicines. 2020 Sep 23;8(10):373. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100373. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32977626 Free PMC article.
-
Current and Emerging Reconstituted HDL-apoA-I and HDL-apoE Approaches to Treat Atherosclerosis.J Pers Med. 2018 Oct 3;8(4):34. doi: 10.3390/jpm8040034. J Pers Med. 2018. PMID: 30282955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Serial Infusions of CER-001, a Pre-β High-Density Lipoprotein Mimetic, on Coronary Atherosclerosis in Patients Following Acute Coronary Syndromes in the CER-001 Atherosclerosis Regression Acute Coronary Syndrome Trial: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Cardiol. 2018 Sep 1;3(9):815-822. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.2121. JAMA Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30046828 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reconstituted Discoidal High-Density Lipoproteins: Bioinspired Nanodiscs with Many Unexpected Applications.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2018 Nov 5;20(12):59. doi: 10.1007/s11883-018-0759-1. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2018. PMID: 30397748 Review.
References
-
- Ishida BY, Frolich J, Fielding CJ. Prebeta-migrating high density lipoprotein: quantitation in normal and hyperlipidemic plasma by solid phase radioimmunoassay following electrophoretic transfer. J Lipid Res. 1987;28(7):778–86. . - PubMed
-
- Castro GR, Fielding CJ. Early incorporation of cell-derived cholesterol into pre-beta-migrating high density Lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1988;27:25–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

