Slit-Dependent Endocytic Trafficking of the Robo Receptor Is Required for Son of Sevenless Recruitment and Midline Axon Repulsion
- PMID: 26335920
- PMCID: PMC4559387
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005402
Slit-Dependent Endocytic Trafficking of the Robo Receptor Is Required for Son of Sevenless Recruitment and Midline Axon Repulsion
Abstract
Understanding how axon guidance receptors are activated by their extracellular ligands to regulate growth cone motility is critical to learning how proper wiring is established during development. Roundabout (Robo) is one such guidance receptor that mediates repulsion from its ligand Slit in both invertebrates and vertebrates. Here we show that endocytic trafficking of the Robo receptor in response to Slit-binding is necessary for its repulsive signaling output. Dose-dependent genetic interactions and in vitro Robo activation assays support a role for Clathrin-dependent endocytosis, and entry into both the early and late endosomes as positive regulators of Slit-Robo signaling. We identify two conserved motifs in Robo's cytoplasmic domain that are required for its Clathrin-dependent endocytosis and activation in vitro; gain of function and genetic rescue experiments provide strong evidence that these trafficking events are required for Robo repulsive guidance activity in vivo. Our data support a model in which Robo's ligand-dependent internalization from the cell surface to the late endosome is essential for receptor activation and proper repulsive guidance at the midline by allowing recruitment of the downstream effector Son of Sevenless in a spatially constrained endocytic trafficking compartment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

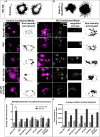
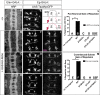
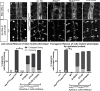
References
-
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, et al. (1999) Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell 96: 795–806. - PubMed
-
- Kidd T, Bland KS, Goodman CS (1999) Slit is the midline repellent for the robo receptor in Drosophila. Cell 96: 785–794. - PubMed
-
- Kidd T, Brose K, Mitchell KJ, Fetter RD, Tessier-Lavigne M, et al. (1998a) Roundabout controls axon crossing of the CNS midline and defines a novel subfamily of evolutionarily conserved guidance receptors. Cell 92: 205–215. - PubMed
-
- Wang KH, Brose K, Arnott D, Kidd T, Goodman CS, et al. (1999) Biochemical purification of a mammalian slit protein as a positive regulator of sensory axon elongation and branching. Cell 96: 771–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

