FOXA1 regulates androgen receptor variant activity in models of castrate-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 26336819
- PMCID: PMC4745762
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4927
FOXA1 regulates androgen receptor variant activity in models of castrate-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
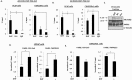
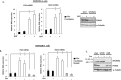
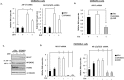
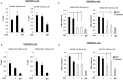
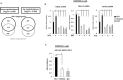
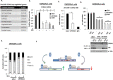
Retention of androgen receptor (AR) signalling in castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) highlights the requirement for the development of more effective AR targeting therapies. A key mechanism of resistance to anti-androgens is through expression of constitutively active AR variants (AR-Vs) that are refractory to next-generation therapies, including Enzalutamide and Abiraterone. By maintaining an androgenic gene signature, AR-Vs drive tumour survival and progression in castrate conditions. Critically, however, our understanding of the mechanics of AR-V-driven transcription is limited, particularly with respect to dependency on pioneer factor function. Here we show that depletion of FOXA1 in the CWR22Rv1 CRPC cell line abrogates the oncogenic potential of AR-Vs. Gene expression profiling reveals that approximately 41% of the AR-V transcriptome requires FOXA1 and that depletion of FOXA1 attenuates AR-V binding at a sub-set of analysed co-regulated genes. Interestingly, AR-V levels are elevated in cells depleted of FOXA1 as a consequence of attenuated negative feedback on the AR gene, but is insufficient to maintain cell growth as evidenced by marked anti-proliferative effects in FOXA1 knockdown cells. In all, our data suggests that AR-Vs are dependent on FOXA1 for sustaining a pro-proliferative gene signature and agents targeting FOXA1 may represent novel therapeutic options for CRPC patients.
Keywords: FOXA1; androgen receptor variants; prostate cancer; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and exploitation of a novel mutant androgen receptor modelling strategy to identify new targets for advanced prostate cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):26029-40. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4347. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26267320 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 Is Implicated in Tumor Progression and Resistance to Anti-androgen Drug Through Regulation of Androgen Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2017 Jan;37(1):125-134. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11297. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28011482
-
Elevated levels of FOXA1 facilitate androgen receptor chromatin binding resulting in a CRPC-like phenotype.Oncogene. 2014 Dec 11;33(50):5666-74. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.508. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24292680 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the mechanisms of androgen deprivation resistance in prostate cancer at the molecular level.Eur Urol. 2015 Mar;67(3):470-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.09.049. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25306226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of drug resistance that target the androgen axis in castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Sep;153:105-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.05.010. Epub 2015 May 29. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26032458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Reveals that the Pioneering Function of FOXA1 Is Independent of Hormonal Signaling.Cell Rep. 2019 Mar 5;26(10):2558-2565.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.036. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30840881 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of AR splice variants through XPO1 suppression contributes to the inhibition of prostate cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 19;9(82):35327-35342. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26239. eCollection 2018 Oct 19. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30450161 Free PMC article.
-
Defining Splicing Factor Requirements for Androgen Receptor Variant Synthesis in Advanced Prostate Cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 3;22(12):1128-1142. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-23-0958. Mol Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39348093 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Prostate Cancer Development: Therapeutic Implications.Medicines (Basel). 2019 Jul 30;6(3):82. doi: 10.3390/medicines6030082. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31366128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic profiling identifies markers of endocrine resistance and therapeutic options for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Jul 15;6(7):102215. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102215. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 40609538 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wong YN, Ferraldeschi R, Attard G, de Bono J. Evolution of androgen receptor targeted therapy for advanced prostate cancer. Nature Reviews. 2014;11:365–376. - PubMed
-
- Mukherji D, Omlin A, Pezaro C, Shamseddine A, de Bono J. Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC): preclinical and clinical evidence for the sequential use of novel therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Reviews. 2014;33:555–566. - PubMed
-
- Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, Taplin ME, Sternberg CN, Miller K, de Wit R, Mulders P, Chi KN, Shore ND, Armstrong AJ, Flaig TW, Flechon A, Mainwaring P, Fleming M, Hainsworth JD, et al. Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1187–1197. - PubMed
-
- Brasso K, Thomsen FB, Schrader AJ, Schmid SC, Lorente D, Retz M, Merseburger AS, von Klot CA, Boegemann M, de Bono J. Enzalutamide Antitumour Activity Against Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Previously Treated with Docetaxel and Abiraterone: A Multicentre Analysis. Eur Urol. 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

