PTP1B-dependent regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by the actin-binding protein Mena
- PMID: 26337385
- PMCID: PMC4626070
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E15-06-0442
PTP1B-dependent regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by the actin-binding protein Mena
Abstract
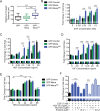
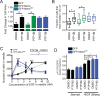
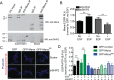
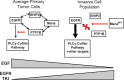
During breast cancer progression, alternative mRNA splicing produces functionally distinct isoforms of Mena, an actin regulator with roles in cell migration and metastasis. Aggressive tumor cell subpopulations express Mena(INV), which promotes tumor cell invasion by potentiating EGF responses. However, the mechanism by which this occurs is unknown. Here we report that Mena associates constitutively with the tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B and mediates a novel negative feedback mechanism that attenuates receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. On EGF stimulation, complexes containing Mena and PTP1B are recruited to the EGFR, causing receptor dephosphorylation and leading to decreased motility responses. Mena also interacts with the 5' inositol phosphatase SHIP2, which is important for the recruitment of the Mena-PTP1B complex to the EGFR. When Mena(INV) is expressed, PTP1B recruitment to the EGFR is impaired, providing a mechanism for growth factor sensitization to EGF, as well as HGF and IGF, and increased resistance to EGFR and Met inhibitors in signaling and motility assays. In sum, we demonstrate that Mena plays an important role in regulating growth factor-induced signaling. Disruption of this attenuation by Mena(INV) sensitizes tumor cells to low-growth factor concentrations, thereby increasing the migration and invasion responses that contribute to aggressive, malignant cell phenotypes.
© 2015 Hughes, Oudin, et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures




Similar articles
-
MenaINV dysregulates cortactin phosphorylation to promote invadopodium maturation.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 8;6:36142. doi: 10.1038/srep36142. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27824079 Free PMC article.
-
MenaINV mediates synergistic cross-talk between signaling pathways driving chemotaxis and haptotaxis.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Oct 15;27(20):3085-3094. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-04-0212. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27559126 Free PMC article.
-
The activated insulin-like growth factor I receptor induces depolarization in breast epithelial cells characterized by actin filament disassembly and tyrosine dephosphorylation of FAK, Cas, and paxillin.Exp Cell Res. 1999 Aug 25;251(1):244-55. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4566. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10438590
-
In control at the ER: PTP1B and the down-regulation of RTKs by dephosphorylation and endocytosis.Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;20(11):672-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.08.013. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Trends Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20864346 Review.
-
Metastasis: tumor cells becoming MENAcing.Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;21(2):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21071226 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal mimicry in tumors: lessons from neuroscience to tackle cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025 Feb 11;44(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s10555-025-10249-3. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025. PMID: 39934425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of miR-130 Family Suppresses Bladder Tumor Growth by Targeting Various Oncogenic Pathways via PTPN1.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4751. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094751. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33947152 Free PMC article.
-
Invadopodia in cancer metastasis: dynamics, regulation, and targeted therapies.J Transl Med. 2025 May 16;23(1):548. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06526-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40380267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin dynamics during tumor cell dissemination.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021;360:65-98. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2020.09.004. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33962751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages in tumor cell migration and metastasis.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 1;15:1494462. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494462. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39555068 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander S, Friedl P. Cancer invasion and resistance: interconnected processes of disease progression and therapy failure. Trends Mol Med. 2012;18:13–26. - PubMed
-
- Avraham R, Yarden Y. Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:104–117. - PubMed
-
- Ball LJ, Jarchau T, Oschkinat H, Walter U. EVH1 domains: structure, function and interactions. FEBS Lett. 2002;513:45–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

