Partial reconstitution of humoral immunity and fewer infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib
- PMID: 26337493
- PMCID: PMC4635117
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-04-639203
Partial reconstitution of humoral immunity and fewer infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Sun C, Tian X, Lee YS, et al. Partial reconstitution of humoral immunity and fewer infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Blood. 2015;126(19):2213-2219.Blood. 2016 Aug 18;128(7):1020. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-06-725010. Blood. 2016. PMID: 31265506 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is characterized by immune dysregulation, often including hypogammaglobulinemia, which contributes to a high rate of infections and morbidity. Ibrutinib, a covalent inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), inhibits B-cell receptor signaling and is an effective, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved treatment of CLL. Inactivating germline mutations in BTK cause a severe B-cell defect and agammaglobulinemia. Therefore, we assessed the impact of ibrutinib on immunoglobulin levels, normal B cells, and infection rate in patients with CLL treated with single-agent ibrutinib on a phase 2 investigator-initiated trial. Consistent with previous reports, immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels remained stable during the first 6 months on treatment, but decreased thereafter. In contrast, there were a transient increase in IgM and a sustained increase in IgA (median increase 45% at 12 months, P < .0001). To distinguish the effects on clonal B cells from normal B cells, we measured serum free light chains (FLCs). In κ-clonal CLL cases, clonal (κ) FLCs were elevated at baseline and normalized by 6 months. Nonclonal (λ) FLCs, which were often depressed at baseline, increased, suggesting the recovery of normal B cells. Consistently, we observed normal B-cell precursors in the bone marrow and an increase in normal B-cell numbers in the peripheral blood. Patients with superior immune reconstitution, as defined by an increase in serum IgA of ≥50% from baseline to 12 months, had a significantly lower rate of infections (P = .03). These data indicate that ibrutinib allows for a clinically meaningful recovery of humoral immune function in patients with CLL. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT015007330.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01500733 NCT15007330 NCT01500733.
Figures
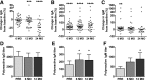


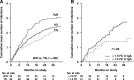
Comment in
-
Ibrutinib in CLL: 2 sides of the same coin.Blood. 2015 Nov 5;126(19):2173-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-670653. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26542251 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Efficacy and Tolerability of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Ibrutinib in Various B-cell Malignancies in the General Community: A Single-center Experience.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017 Jul;17S:S53-S61. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.02.011. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017. PMID: 28760303
-
Etiology of Ibrutinib Therapy Discontinuation and Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.JAMA Oncol. 2015 Apr;1(1):80-7. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2014.218. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26182309 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of humoral immunity and decreased risk of infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Leuk Lymphoma. 2020 Oct;61(10):2375-2382. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2020.1772477. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020. PMID: 32508208 Free PMC article.
-
Ibrutinib: a new frontier in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia by Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibition.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2013 Dec;11(4):265-71. doi: 10.2174/1871525712666140115143914. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24433470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ibrutinib for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma.Drugs Today (Barc). 2014 Apr;50(4):291-300. doi: 10.1358/dot.2014.50.4.2133570. Drugs Today (Barc). 2014. PMID: 24918646 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2021 Jun 10;137(23):3165-3173. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021011568. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33861303 Free PMC article.
-
TH2/TH1 Shift Under Ibrutinib Treatment in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 15;11:637186. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.637186. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33937038 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients treated with either Ibrutinib or Rituximab.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Jun;23(2):371-379. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00809-0. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 35352210 Free PMC article.
-
Promises and pitfalls of targeted agents in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Cancer Drug Resist. 2020 May 23;3(3):415-444. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.108. eCollection 2020. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 35582452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporary cessation of ibrutinib results in reduced grade 3-4 infections and durable remissions-Interim analysis of an on-off-repeat Phase 1b/2 study in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.EJHaem. 2021 Jul 14;2(3):525-529. doi: 10.1002/jha2.261. eCollection 2021 Aug. EJHaem. 2021. PMID: 35844699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morrison VA. Infectious complications in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: pathogenesis, spectrum of infection, and approaches to prophylaxis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2009;9(5):365–370. - PubMed
-
- Zinneman HH, Hall WH, Heller BI. Acquired agammaglobulinemia: report of three cases. J Am Med Assoc. 1954;156(15):1390–1393. - PubMed
-
- Jim RT, Reinhard EH. Agammaglobulinemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1956;44(4):790–796. - PubMed
-
- Hamblin AD, Hamblin TJ. The immunodeficiency of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br Med Bull. 2008;87:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Freeman JA, Crassini KR, Best OG, et al. Immunoglobulin G subclass deficiency and infection risk in 150 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54(1):99–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

