Transcriptional regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- PMID: 26337512
- PMCID: PMC4661041
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.4RI0515-204R
Transcriptional regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
Abstract
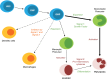
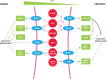
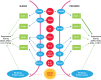
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells are a heterogeneous group of pathologically activated immature cells that play a major role in the negative regulation of the immune response in cancer, autoimmunity, many chronic infections, and inflammatory conditions, as well as in the regulation of tumor angiogenesis, tumor cell invasion, and metastases. Accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells is governed by a network of transcriptional regulators that could be combined into 2 partially overlapping groups: factors promoting myelopoiesis and preventing differentiation of mature myeloid cells and factors promoting pathologic activation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. In this review, we discuss the specific nature of these factors and their impact on myeloid-derived suppressor cell development.
Keywords: Rb1; S100A9; STAT3; STAT6.
© Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Figures
References
-
- Lee M. Y., Rosse C. (1982) Depletion of lymphocyte subpopulations in primary and secondary lymphoid organs of mice by a transplanted granulocytosis-inducing mammary carcinoma. Cancer Res. 42, 1255–1260. - PubMed
-
- Tsuchiya Y., Igarashi M., Suzuki R., Kumagai K. (1988) Production of colony-stimulating factor by tumor cells and the factor-mediated induction of suppressor cells. J. Immunol. 141, 699–708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

