Relation between reperfusion and hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 26337766
- PMCID: PMC4648971
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-015-1577-6
Relation between reperfusion and hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Introduction: Intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (IV-rtPA) is given in acute ischemic stroke patients to achieve reperfusion. Hemorrhagic transformation (HT) is a serious complication of IV-rtPA treatment and related to blood-brain barrier (BBB) injury. It is unclear whether HT occurs secondary to reperfusion in combination with ischemic BBB injury or is caused by the negative effect of IV-rtPA on BBB integrity. The aim of this study was to establish the association between reperfusion and the occurrence of HT.
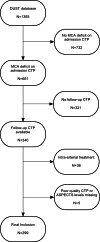
Methods: From the DUST study, patients were selected with admission and follow-up non-contrast CT (NCCT) and CT perfusion (CTP) imaging, and a perfusion deficit in the middle cerebral artery territory on admission. Reperfusion was categorized qualitatively as reperfusion or no-reperfusion by visual comparison of admission and follow-up CTP. Occurrence of HT was assessed on follow-up NCCT. The association between reperfusion and occurrence of HT on follow-up was estimated by calculating odds ratios (ORs) and 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) with additional stratification for IV-rtPA treatment.
Results: Inclusion criteria were met in 299 patients. There was no significant association between reperfusion and HT (OR 1.2 95%CI 0.5-3.1). In patients treated with IV-rtPA (n = 203), the OR was 1.3 (95%CI 0.4-4.0), and in patients not treated with IV-rtPA (n = 96), the OR was 0.8 (95%CI 0.1-4.5). HT occurred in 14 % of the IV-rtPA patients and in 7 % of patients without IV-rtPA (95%CI of difference -1 to 14 %).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the increased risk of HT after acute ischemic stroke treatment is not dependent on the reperfusion status.
Keywords: CT perfusion; Hemorrhagic transformation; Ischemic stroke; Reperfusion; rtPA.
References
-
- Albers GW, Thijs VN, Wechsler L, Kemp S, Schlaug G, Skalabrin E, Bammer R, Kakuda W, Lansberg MG, Shuaib A, Coplin W, Hamilton S, Moseley M, Marks MP. Magnetic resonance imaging profiles predict clinical response to early reperfusion: the diffusion and perfusion imaging evaluation for understanding stroke evolution (DEFUSE) study. Ann Neurol. 2006;60(5):508–517. doi: 10.1002/ana.20976. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soares BP, Tong E, Hom J, Cheng SC, Bredno J, Boussel L, Smith WS, Wintermark M. Reperfusion is a more accurate predictor of follow-up infarct volume than recanalization: a proof of concept using CT in acute ischemic stroke patients. Stroke. 2010;41:e34–40. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.568766. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous