Hypertension Control Cascade: A Framework to Improve Hypertension Awareness, Treatment, and Control
- PMID: 26337797
- PMCID: PMC5049660
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12654
Hypertension Control Cascade: A Framework to Improve Hypertension Awareness, Treatment, and Control
Abstract
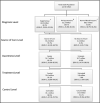
Evidence-based interventions differ for increasing hypertension awareness, treatment, and control and should be targeted for specific patient panels. This study developed a hypertension control cascade to identify patients with a usual source of care represented at each level of the cascade using the 2007-2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Overall, 10.7 million adults in the United States were unaware of their condition, 3.8 million were aware but untreated, and 15.8 million were treated but uncontrolled. The results also suggest that failure to attain hypertension control because of lack of awareness or lack of treatment despite awareness occurs mainly among younger individuals and those with no annual healthcare visits, while the elderly and minorities are more likely to remain uncontrolled when aware and treated. Opportunities to leverage population health management functions in electronic health information systems to align the specific patient subgroups facing barriers to hypertension control at each level of the cascade with targeted hypertension management interventions are discussed.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Nwankwo T, Yoon S, Burt V, Gu Q. Hypertension among adults in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011‐2012. NCHS Data Brief. 2013;133:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Farley TA, Dalal MA, Mostashari F, Frieden TR. Deaths preventable in the US by improvements in use of clinical preventive services. Am J Prev Med. 2010;38:600–609. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

