Pharmacokinetics and safety of ixazomib plus lenalidomide-dexamethasone in Asian patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma: a phase 1 study
- PMID: 26337806
- PMCID: PMC4559079
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-015-0198-1
Pharmacokinetics and safety of ixazomib plus lenalidomide-dexamethasone in Asian patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma: a phase 1 study
Abstract
Background: The oral proteasome inhibitor ixazomib is under phase 3 clinical investigation in multiple myeloma (MM) in combination with lenalidomide-dexamethasone. This study was conducted to investigate the pharmacokinetic and safety profiles of ixazomib, administered with lenalidomide-dexamethasone, in East Asian patients with relapsed/refractory MM.
Methods: Adult patients with measurable disease who had received 1-3 prior lines of therapy received oral ixazomib on days 1, 8, and 15, lenalidomide (25 mg) on days 1-21, and dexamethasone (40 mg) on days 1, 8, 15, and 22, in 28-day cycles. Primary objectives were to characterize ixazomib plasma pharmacokinetics, determine the recommended phase 2/3 dose, and evaluate safety and tolerability.
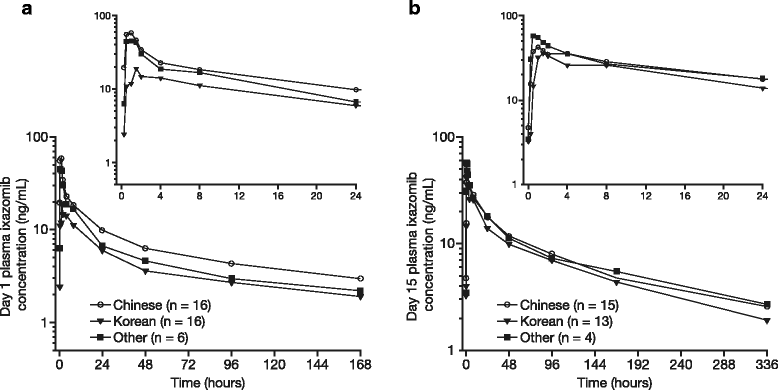
Results: Forty-three patients were enrolled. No dose-limiting toxicities were reported for the first six patients receiving ixazomib (4.0 mg), confirming this as the recommended phase 2/3 dose. Ixazomib was rapidly absorbed with a median T max of 1.5 h on day 1 and 2.0 h on day 15 of cycle 1 and had a geometric mean terminal half-life of 6.1 days. Twenty-one (49%) patients had at least one drug-related grade ≥3 adverse event (AE); the most common were neutropenia (19%), diarrhea (14%), and thrombocytopenia (12%). Twenty-eight of 43 (65%) response-evaluable patients had at least a partial response. The recommended phase 2/3 dose for ixazomib was determined to be 4.0 mg.
Conclusions: The all-oral combination of ixazomib plus lenalidomide-dexamethasone appeared active and well tolerated at 4.0 mg. Consequently, East Asian patients enrolled in phase 3 studies are receiving the same ixazomib dose as patients in other regions.
Trial registration: This study is registered at NCT01645930.
Figures

References
-
- Cavo M, Tacchetti P, Patriarca F, Petrucci MT, Pantani L, Galli M, et al. Bortezomib with thalidomide plus dexamethasone compared with thalidomide plus dexamethasone as induction therapy before, and consolidation therapy after, double autologous stem-cell transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a randomised phase 3 study. Lancet. 2010;376(9758):2075–85. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61424-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cavo M, Pantani L, Petrucci MT, Patriarca F, Zamagni E, Donnarumma D, et al. Bortezomib-thalidomide-dexamethasone is superior to thalidomide-dexamethasone as consolidation therapy after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;120(1):9–19. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-408898. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jakubowiak AJ, Dytfeld D, Griffith KA, Lebovic D, Vesole DH, Jagannath S, et al. A phase 1/2 study of carfilzomib in combination with lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone as a frontline treatment for multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;120(9):1801–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-422683. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

