Standardised formal resuscitation training programmes for reducing mortality and morbidity in newborn infants
- PMID: 26337958
- PMCID: PMC9219024
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009106.pub2
Standardised formal resuscitation training programmes for reducing mortality and morbidity in newborn infants
Abstract
Background: Approximately 10% of all newborns require resuscitation at birth. Training healthcare providers in standardised formal neonatal resuscitation training (SFNRT) programmes may improve neonatal outcomes. Substantial healthcare resources are expended on SFNRT.
Objectives: To determine whether SFNRT programmes reduce neonatal mortality and morbidity, improve acquisition and retention of knowledge and skills, or change teamwork and resuscitation behaviour.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, PREMEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, Web of Science and the Oxford Database of Perinatal Trials, ongoing trials and conference proceedings in April 2014 and updated in March 2015.
Selection criteria: Randomised or quasi-randomised trials including cluster-randomised trials, comparing a SFNRT with no SFNRT, additions to SFNRT or types of SFNRT, and reporting at least one of our specified outcomes.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors extracted data independently and performed statistical analyses including typical risk ratio (RR), risk difference (RD), mean difference (MD), and number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) or an additional harmful outcome (NNTH) (all with 95% confidence intervals (CI)). We analysed cluster-randomised trials using the generic inverse variance and the approximate analysis methods.
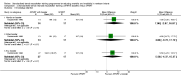
Main results: We identified two community-based and three manikin-based trials that assessed the effect of SFNRT compared with no SFNRT. Very low quality evidence from one study suggested improvement in acquisition of knowledge (RR 5.96, 95% CI 3.60 to 9.87) and skills (RR 170, 95% CI 10.8 to 2711) and retention of knowledge (RR 3.60, 95% CI 2.43 to 5.35) and the other study suggested improvement in resuscitation and behavioural scores.We identified three community-based cluster-randomised trials in developing countries comparing SFNRT with basic resuscitation training (Early Newborn Care). In this setting, there was moderate quality evidence that SFNRT decreased early neonatal mortality (typical RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.00; 3 studies, 66,162 neonates) and when analysed by the approximate analysis method (typical RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.75 to 0.96; RD -0.0044, 95% CI -0.0082 to -0.0006; NNTB 227, 95% CI 122 to 1667). Low quality evidence from one trial showed that SFNRT may decrease 28-day mortality (typical RR 0.55, 95% CI 0.33 to 0.91) but the effect on late neonatal mortality was more uncertain (typical RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.20 to 1.11). None of our a priori defined neonatal morbidities were reported. We did not identify any randomised studies in the developed world.We identified two trials that compared SFNRT with team training to SFNRT. Teamwork training of physician trainees with simulation may increase any teamwork behaviour (assessed by frequency) (MD 2.41, 95% CI 1.72 to 3.11) and decrease resuscitation duration (MD -149.54, 95% CI -214.73 to -84.34) but may lead to little or no difference in Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) scores (MD 1.40, 95% CI -2.02 to 4.82; 98 participants, low quality evidence).We identified two trials that compared SFNRT with booster courses to SFNRT. It is uncertain whether booster courses improve retention of resuscitation knowledge (84 participants, very low quality evidence) but may improve procedural and behavioural skills (40 participants, very low quality evidence).We identified two trials on decision support tools, one on a cognitive aid that did not change resuscitation scores and the other on an electronic decision support tool that improved the frequency of correct decision making on positive pressure ventilation, cardiac compressions and frequency of fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) adjustments (97 participants, very low quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions: SFNRT compared to basic newborn care or basic newborn resuscitation, in developing countries, results in a reduction of early neonatal and 28-day mortality. Randomised trials of SFNRT should report on neonatal morbidity including hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy and neurodevelopmental outcomes. Innovative educational methods that enhance knowledge and skills and teamwork behaviour should be evaluated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
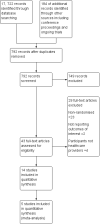

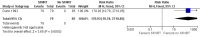
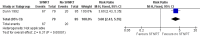



















Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bender 2014 {published data only}
Bould 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bould MD, Hayter MA, Campbell DM, Chandra DB, Joo HS, Naik VN. Cognitive aid for neonatal resuscitation: a prospective single‐blinded randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2009;103(4):570‐5. - PubMed
Carlo 2010a {published data only}
-
- Goudar SS, Dhaded SM, McClure EM, Derman RJ, Patil VD, Mahantshetti NS, et al. ENC training reduces perinatal mortality in Karnataka, India. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2012;25(6):568‐74. - PubMed
Carlo 2010b {published data only}
Dunn 1992 {published data only}
-
- Dunn S, Niday P, Watters NE, McGrath P, Alcock D. The provision and evaluation of a neonatal resuscitation program. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1992;23(3):118‐26. - PubMed
Fuerch 2015 {published data only}
-
- Fuerch JH, Yamada NK, Coelho PR, Lee HC, Halamek LP. Impact of a novel decision support tool on adherence to Neonatal Resuscitation Program algorithm. Resuscitation 2015;88:52‐6. - PubMed
Gill 2011 {published data only}
Kaczorowski 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kaczorowski J, Levitt C, Hammond M, Outerbridge E, Grad R, Rothman A, et al. Retention of neonatal resuscitation skills and knowledge: a randomized controlled trial. Family Medicine 1998;30(10):705‐11. - PubMed
Lee 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lee M, Brown L, Bender J, Machan J, Overly F. A medical simulation‐based educational intervention for emergency medicine residents in neonatal resuscitation. Academic Emergency Medicine 2012;19:577‐85. - PubMed
Opiyo 2008 {published data only}
Rubio‐Gurung 2014 {published data only}
-
- Rubio‐Gurung S, Putet G, Touzet S, Gauthier‐Moulinier H, Jordan I, Beissel A, et al. In situ simulation training for neonatal resuscitation: an RCT. Pediatrics 2014;134(3):e790‐7. [PUBMED: 25092937] - PubMed
Thomas 2007 {published data only}
-
- Thomas EJ, Taggart B, Crandell S, Lasky RE, Williams AL, Love LJ, et al. Teaching teamwork during the Neonatal Resuscitation Program: a randomized trial. Journal of Perinatology 2007;27(7):409‐14. - PubMed
Thomas 2010 {published data only}
-
- Thomas EJ, Williams AL, Reichman EF, Lasky RE, Crandell S, Taggart WR. Team training in the neonatal resuscitation program for interns: teamwork and quality of resuscitations. Pediatrics 2010;125(3):539‐46. - PubMed
Xu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Xu T, Wang H, Gong L, Ye H, Yu R, Wang D, et al. The impact of an intervention package promoting effective neonatal resuscitation training in rural China. Resuscitation 2014;85(2):253‐9. [AN: 2014062624 ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ashish 2012 {published data only}
Boo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Boo NY. Neonatal resuscitation programme in Malaysia: an eight‐year experience. Singapore Medical Journal 2009;50(2):152‐9. - PubMed
Carlo 2010c {published data only}
-
- Carlo WA, McClure EM, Chomba E, Chakraborty H, Hartwell T, Harris H, et al. Newborn care training of midwives and neonatal and perinatal mortality rates in a developing country. Pediatrics 2010;126(5):e1064‐71. - PubMed
Cavaleiro 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cavaleiro A, Guimaraes H, Calheiros F. Training neonatal skills with simulators?. Acta Paediatrica 2009;98(4):636‐9. - PubMed
Chomba 2008 {published data only}
Curran 2015 {published data only}
-
- Curran V, Fleet L, White S, Bessell C, Deshpandey A, Drover A, et al. A randomized controlled study of manikin simulator fidelity on neonatal resuscitation program learning outcomes. Advances in Health Sciences Education: Theory and Practice 2015;20(1):205‐18. [DOI: 10.1007/s10459-014-9522-8; PUBMED: 24916954] - DOI - PubMed
Deindl 2015 {published data only}
-
- Deindl P, Schwindt J, Berger A, Schmolzer GM. An instructional video enhanced bag‐mask ventilation quality during simulated newborn resuscitation. Acta Paediatrica, International Journal of Paediatrics 2015;104(1):e20‐6. [AN: 2015643641 ] - PubMed
Deorari 2001 {published data only}
-
- Deorari AK, Paul VK, Singh M, Vidyasagar D. Impact of education and training on neonatal resuscitation practices in 14 teaching hospitals in India. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2001;21(1):29‐33. - PubMed
Duran 2008a {published data only}
-
- Duran R, Aladag N, Vatansever U, Sut N, Acunas B. The impact of Neonatal Resuscitation Program courses on mortality and morbidity of newborn infants with perinatal asphyxia. Brain & Development 2008;30(1):43‐6. - PubMed
Duran 2008b {published data only}
-
- Duran R, Aladag N, Vatansever U, Kucukugurluoglu Y, Sut N, Acunas B. Proficiency and knowledge gained and retained by pediatric residents after neonatal resuscitation course. Pediatrics International 2008;50(5):644‐7. - PubMed
Durojaiye 2002 {published data only}
-
- Durojaiye L, O'Meara M. Improvement in resuscitation knowledge after a one‐day paediatric life‐support course. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2002;38(3):241‐5. - PubMed
Ergenekon 2000 {published data only}
-
- Ergenekon E, Koc E, Atalay Y, Soysal S. Neonatal resuscitation course experience in Turkey. Resuscitation 2000;45(3):225‐7. - PubMed
Ersdal 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ersdal HL, Vossius C, Bayo E, Mduma E, Perlman J, Lippert A, et al. A one‐day "Helping Babies Breathe" course improves simulated performance but not clinical management of neonates. Resuscitation 2013;84(10):1422‐7. - PubMed
Finan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Finan E, Bismilla Z, Whyte H, LeBlanc V, McNamara P. High‐fidelity simulator technology may not be superior to traditional low‐fidelity equipment for neonatal resuscitation training. Journal of Perinatology 2012;32(4):287‐92. - PubMed
Goudar 2013 {published data only}
-
- Goudar SS, Somannavar MS, Clark R, Lockyer JM, Revankar AP, Fidler HM, et al. Stillbirth and newborn mortality in India after helping babies breathe training. Pediatrics 2013;131(2):e344‐52. - PubMed
Hubballi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hubballi JG, Sumitra LA, Raddi SA. Randomized control trial to evaluate the effectiveness of Helping Babies Breathe Programme on knowledge and skills regarding neonatal resuscitation among auxiliary nurse midwives students. International Journal of Nursing Education 2014;6(1):146‐51. [DOI: ]
López‐Herce 1999 {published data only}
-
- López‐Herce J, Carrillo A, Rodriguez A, Calvo C, Delgado MA, Tormo C. Paediatric life support instructors courses in Spain. Spanish Paediatric and Neonatal Resuscitation Group. Resuscitation 1999;41(2):205‐9. - PubMed
Mathai 2015 {published data only}
Msemo 2013 {published data only}
-
- Msemo G, Massawe A, Mmbando D, Rusibamayila N, Manji K, Kidanto HL, et al. Newborn mortality and fresh stillbirth rates in Tanzania after helping babies breathe training. Pediatrics 2013;131(2):e353‐60. - PubMed
Nadler 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nadler I, Sanderson PM, Dyken CR, Davis PG, Liley HG. Presenting video recordings of newborn resuscitations in debriefings for teamwork training. British Medical Journal Quality & Safety 2011;20(2):163‐9. - PubMed
Patel 2001 {published data only}
-
- Patel D, Piotrowski ZH, Nelson MR, Sabich R. Effect of a statewide neonatal resuscitation training program on Apgar scores among high‐risk neonates in Illinois. Pediatrics 2001;107(4):648‐55. - PubMed
Patel 2002 {published data only}
-
- Patel D, Piotrowski ZH. Positive changes among very low birth weight infant Apgar scores that are associated with the Neonatal Resuscitation Program in Illinois. Journal of Perinatology 2002;22(5):386‐90. - PubMed
Senarath 2007 {published data only}
-
- Senarath U, Fernando DN, Rodrigo I. Effect of training for care providers on practice of essential newborn care in hospitals in Sri Lanka. Journal of Obstetric Gynecologic & Neonatal Nursing 2007;36:531‐41. - PubMed
Singhal 2001 {published data only}
-
- Singhal N, McMillan DD, Yee WH, Akierman AR, Yee YJ. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the standardized neonatal resuscitation program. Journal of Perinatology 2001;21(6):388‐92. - PubMed
Skidmore 2001 {published data only}
Tan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Tan S, Batey N, Sharkey D. Cardiac compression quality deteriorates with increasing compression rate during preterm resuscitation simulations: a new preterm simulation trainer. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2014;99:A71. [AN: 71666433 ]
Trevisanuto 2005 {published data only}
-
- Trevisanuto D, Ferrarese P, Cavicchioli P, Fasson A, Zanardo V, Zacchello F. Knowledge gained by pediatric residents after neonatal resuscitation program courses. Paediatric Anaesthesia 2005;15(11):944‐7. - PubMed
Trevisanuto 2007 {published data only}
-
- Trevisanuto D, Ibrahim SA, Doglioni N, Salvadori S, Ferrarese P, Zanardo V. Neonatal resuscitation courses for pediatric residents: comparison between Khartoum (Sudan) and Padova (Italy). Paediatric Anaesthesia 2007;17(1):28‐31. - PubMed
Walker 2014 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Campbell 2014 {published data only}
-
- Campbell DM, Finan E. Impact of video‐debriefing following simulated neonatal resuscitation in inter‐professional teams. Paediatrics and Child Health (Canada) 2014;19:e88. [AN: 71621217]
Yamada 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yamada NK, Fuerch JH, Halamek LP. Impact of standardized communication techniques on errors during simulated neonatal resuscitation. Journal of Investigative Medicine 2015;66:99‐100. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Bang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bang A, Bellad R, Gisore P, Hibberd P, Patel A, Goudar S, et al. Implementation and evaluation of the Helping Babies Breathe curriculum in three resource limited settings: does Helping Babies Breathe save lives? A study protocol. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2014;14(1):116. [AN: 2014284423] - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
AHA 2000
-
- American Heart Association and International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation. Guidelines 2000 for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Part 11: neonatal resuscitation. Circulation 2000;102(8 Suppl):I343‐57. - PubMed
Bell 2008
Chance 1987
Cleary 1998
-
- Cleary GM, Wiswell TE. Meconium‐stained amniotic fluid and the meconium aspiration syndrome. An update. Pediatric Clinics of North America 1998;45(3):511‐29. - PubMed
de Almeida 2014
-
- Almeida M, Guinsburg R, Sancho G, Rosa I, Lamy Z, Martinez F, et al. Hypothermia and early neonatal mortality in preterm infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2014;164(2):271‐5. - PubMed
Estol 1992
-
- Estol PC, Piriz H, Basalo S, Simini F, Grela C. Oro‐naso‐pharyngeal suction at birth: effects on respiratory adaptation of normal term vaginally born infants. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 1992;20(4):297‐305. - PubMed
Goudar 2012
-
- Goudar SS, Dhaded SM, McClure EM, Derman RJ, Patil VD, Mahantshetti NS, et al. ENC training reduces perinatal mortality in Karnataka, India. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2012;25(6):568‐74. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
ILCOR 2006
-
- International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation. The International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) consensus on science with treatment recommendations for pediatric and neonatal patients: neonatal resuscitation. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):e978‐88. - PubMed
IMF 2012
-
- International Monetary Fund. Gross domestic product, current prices & gross domestic product based on purchasing‐power‐parity (PPP) valuation of country GD. World Economic Outlook Database. April 2012.
Jabbour 1996
-
- Jabbour M, Osmond MH, Klassen TP. Life support courses: are they effective?. Annals of Emergency Medicine 1996;28(6):690‐8. - PubMed
Knippenberg 2005
-
- Knippenberg R, Lawn JE, Darmstadt GL, Begkoyian G, Fogstad H, Walelign N, et al for the Lancet Neonatal Survival Steering Team. Systematic scaling up of neonatal care in countries. Lancet 2005;365(9464):1087‐98. - PubMed
Lawn 2005
-
- Lawn J, Cousens S, Zupan J. 4 million neonatal deaths: when? where? why?. Lancet 2005;365:891‐900. - PubMed
Lee 2011
-
- Lee AC, Cousens S, Wall SN, Niermeyer S, Darmstadt GL, Carlo WA, et al. Neonatal resuscitation and immediate newborn assessment and stimulation for the prevention of neonatal deaths: a systematic review, meta‐analysis and Delphi estimation of mortality effect. Biomed Central Public Health 2011;11(Suppl 3):S12. - PMC - PubMed
Matendo 2011
Meaney 2010
-
- Meaney PA, Topjian AA, Chandler HK, Botha M, Soar J, Berg RA, et al. Resuscitation training in developing countries: a systematic review. Resuscitation 2010;81(11):1462‐72. - PubMed
Mileder 2014
Narayanan 2004
-
- Narayanan I, Rose M, Cordero D, Faillace S, Sanghvian T. The Components of Essential Newborn Care. Published by Basics Support for Institutionalizing Child Survival Project (BASICS II) for the United States Agency for International Development. Arlington, Virginia. 2004.
Opiyo 2010
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Shankaran 2005
-
- Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole‐body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic‐ischemic encephalopathy. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353(15):1574‐84. - PubMed
Vain 2004
-
- Vain NE, Szyld EG, Prudent LM, Wiswell TE, Aguilar AM, Vivas NI. Oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal suctioning of meconium‐stained neonates before delivery of their shoulders: multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;364(9434):597‐602. - PubMed
Wax 2010
-
- Wax JR, Lucas FL, Lamont M, Pinette MG, Cartin A, Blackstone J. Maternal and newborn outcomes in planned home birth vs planned hospital births: a meta‐analysis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2010;203(3):243.e1‐8. - PubMed
Wiswell 2000
-
- Wiswell TE, Gannon CM, Jacob J, Goldsmith L, Szyld E, Weiss K, et al. Delivery room management of the apparently vigorous meconium‐stained neonate: results of the multicenter, international collaborative trial. Pediatrics 2000;105(1 Pt 1):1‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

