Isothermal Recombinase Polymerase amplification (RPA) of Schistosoma haematobium DNA and oligochromatographic lateral flow detection
- PMID: 26338510
- PMCID: PMC4559068
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-015-1055-3
Isothermal Recombinase Polymerase amplification (RPA) of Schistosoma haematobium DNA and oligochromatographic lateral flow detection
Abstract
Background: Accurate diagnosis of urogenital schistosomiasis is vital for surveillance/control programs. Amplification of schistosome DNA in urine by PCR is sensitive and specific but requires infrastructure, financial resources and skilled personnel, often not available in endemic areas. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) is an isothermal DNA amplification/detection technology that is simple, rapid, portable and needs few resources.
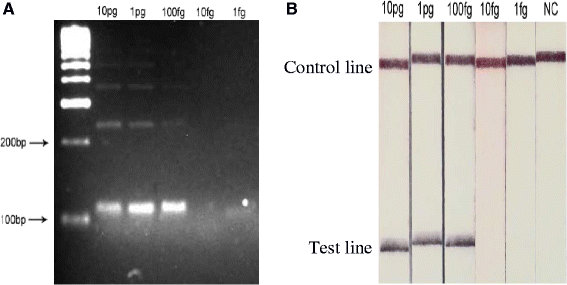
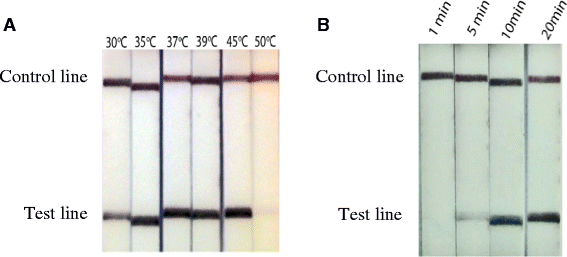
Findings: Here a Schistosoma haematobium RPA assay was developed and adapted so that DNA amplicons could be detected using oligochromatographic Lateral Flow (LF) strips. The assay successfully amplified S. haematobium DNA at 30-45 °C in 10 mins and was sensitive to a lower limit of 100 fg of DNA. The assay was also successful with the addition of crude urine, up to 5% of the total reaction volume. Cross amplification occurred with other schistosome species but not with other common urine microorganisms.
Conclusion: The LF-RPA assay developed here can amplify and detect low levels of S. haematobium DNA. Reactions are rapid, require low temperatures and positive reactions are interpreted using lateral flow strips, reducing the need for infrastructure and resources. This together with an ability to withstand inhibitors within urine makes RPA a promising technology for further development as a molecular diagnostic tool for urogenital schistosomiasis.
Figures
References
-
- Shiff C, Veltri R, Naples J, Quartey J, Otchere J, Anyan W, et al. Ultrasound verification of bladder damage is associated with known biomarkers of bladder cancer in adults chronically infected with Schistosoma haematobium in Ghana. Trans Roy Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006;100(9):847–54. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.10.010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

