The Daxx/Atrx Complex Protects Tandem Repetitive Elements during DNA Hypomethylation by Promoting H3K9 Trimethylation
- PMID: 26340527
- PMCID: PMC4571182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.07.022
The Daxx/Atrx Complex Protects Tandem Repetitive Elements during DNA Hypomethylation by Promoting H3K9 Trimethylation
Abstract
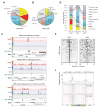
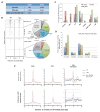
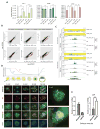
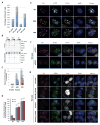
In mammals, DNA methylation is essential for protecting repetitive sequences from aberrant transcription and recombination. In some developmental contexts (e.g., preimplantation embryos) DNA is hypomethylated but repetitive elements are not dysregulated, suggesting that alternative protection mechanisms exist. Here we explore the processes involved by investigating the role of the chromatin factors Daxx and Atrx. Using genome-wide binding and transcriptome analysis, we found that Daxx and Atrx have distinct chromatin-binding profiles and are co-enriched at tandem repetitive elements in wild-type mouse ESCs. Global DNA hypomethylation further promoted recruitment of the Daxx/Atrx complex to tandem repeat sequences, including retrotransposons and telomeres. Knockdown of Daxx/Atrx in cells with hypomethylated genomes exacerbated aberrant transcriptional de-repression of repeat elements and telomere dysfunction. Mechanistically, Daxx/Atrx-mediated repression seems to involve Suv39h recruitment and H3K9 trimethylation. Our data therefore suggest that Daxx and Atrx safeguard the genome by silencing repetitive elements when DNA methylation levels are low.
Keywords: ATRX; DAXX; DNA methylation; DNMTs; histone modification; mouse embryonic stem cells; repetitive sequences; telomeres.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
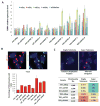
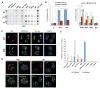
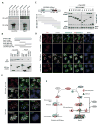
Comment in
-
Adaption by Rewiring Epigenetic Landscapes.Cell Stem Cell. 2015 Sep 3;17(3):249-50. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.08.015. Cell Stem Cell. 2015. PMID: 26340521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armour JA, Anttinen T, May CA, Vega EE, Sajantila A, Kidd JR, Kidd KK, Bertranpetit J, Paabo S, Jeffreys AJ. Minisatellite diversity supports a recent African origin for modern humans. Nat Genet. 1996;13:154–160. - PubMed
-
- Azzalin CM, Reichenbach P, Khoriauli L, Giulotto E, Lingner J. Telomeric repeat containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends. Science. 2007;318:798–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

