Functions and regulation of the multitasking FANCM family of DNA motor proteins
- PMID: 26341555
- PMCID: PMC4573851
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.266593.115
Functions and regulation of the multitasking FANCM family of DNA motor proteins
Abstract
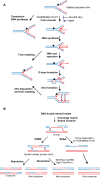
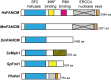
Members of the conserved FANCM family of DNA motor proteins play key roles in genome maintenance processes. FANCM supports genome duplication and repair under different circumstances and also functions in the ATR-mediated DNA damage checkpoint. Some of these roles are shared among lower eukaryotic family members. Human FANCM has been linked to Fanconi anemia, a syndrome characterized by cancer predisposition, developmental disorder, and bone marrow failure. Recent studies on human FANCM and its orthologs from other organisms have provided insights into their biological functions, regulation, and collaboration with other genome maintenance factors. This review summarizes the progress made, with the goal of providing an integrated view of the functions and regulation of these enzymes in humans and model organisms and how they advance our understanding of genome maintenance processes.
Keywords: BLM; FANCM; Fml1; MHF; Mph1; crossover control; replication fork regression.
© 2015 Xue et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Bakker ST, van de Vrugt HJ, Rooimans MA, Oostra AB, Steltenpool J, Delzenne-Goette E, van der Wal A, van der Valk M, Joenje H, te Riele H, et al. 2009. Fancm-deficient mice reveal unique features of Fanconi anemia complementation group M. Hum Mol Genet 18: 3484–3495. - PubMed
-
- Blackford AN, Schwab RA, Nieminuszczy J, Deans AJ, West SC, Niedzwiedz W. 2012. The DNA translocase activity of FANCM protects stalled replication forks. Hum Mol Genet 21: 2005–2016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM057814/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA92584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES007061/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- GM080670/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ES015632/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM057814/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015632/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM080670/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA092584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES007061/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
