Pro-oncogenic Roles of HLXB9 Protein in Insulinoma Cells through Interaction with Nono Protein and Down-regulation of the c-Met Inhibitor Cblb (Casitas B-lineage Lymphoma b)
- PMID: 26342078
- PMCID: PMC4646204
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.661413
Pro-oncogenic Roles of HLXB9 Protein in Insulinoma Cells through Interaction with Nono Protein and Down-regulation of the c-Met Inhibitor Cblb (Casitas B-lineage Lymphoma b)
Abstract
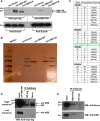
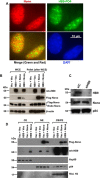
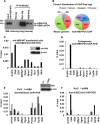
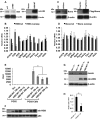
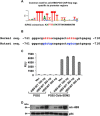
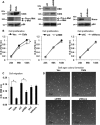
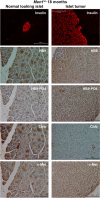
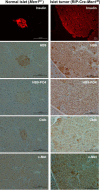
Pancreatic islet β-cells that lack the MEN1-encoded protein menin develop into tumors. Such tumors express the phosphorylated isoform of the β-cell differentiation transcription factor HLXB9. It is not known how phospho-HLXB9 acts as an oncogenic factor in insulin-secreting β-cell tumors (insulinomas). In this study we investigated the binding partners and target genes of phospho-HLXB9 in mouse insulinoma MIN6 β-cells. Co-immunoprecipitation coupled with mass spectrometry showed a significant association of phospho-HLXB9 with the survival factor p54nrb/Nono (54-kDa nuclear RNA-binding protein, non-POU-domain-containing octamer). Endogenous phospho-HLXB9 co-localized with endogenous Nono in the nucleus. Overexpression of HLXB9 decreased the level of overexpressed Nono but not endogenous Nono. Anti-phospho-HLXB9 chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by deep sequencing (ChIP-Seq) identified the c-Met inhibitor, Cblb, as a direct phospho-HLXB9 target gene. Phospho-HLXB9 occupied the promoter of Cblb and reduced the expression of Cblb mRNA. Cblb overexpression or HLXB9 knockdown decreased c-Met protein and reduced cell migration. Also, increased phospho-HLXB9 coincided with reduced Cblb and increased c-Met in insulinomas of two mouse models of menin loss. These data provide mechanistic insights into the role of phospho-HLXB9 as a pro-oncogenic factor by interacting with a survival factor and by promoting the oncogenic c-Met pathway. These mechanisms have therapeutic implications for reducing β-cell proliferation in insulinomas by inhibiting phospho-HLXB9 or its interaction with Nono and modulating the expression of its direct (Cblb) or indirect (c-Met) targets. Our data also implicate the use of pro-oncogenic activities of phospho-HLXB9 in β-cell expansion strategies to alleviate β-cell loss in diabetes.
Keywords: PNET; c-Met; gene regulation; menin (MEN1); neuroendocrine; p54nrb/Nono; pancreatic islet; pathogenesis; phospho-HLXB9; tumor.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Thakker R. V. (2010) Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 24, 355–370 - PubMed
-
- Jiao Y., Shi C., Edil B. H., de Wilde R. F., Klimstra D. S., Maitra A., Schulick R. D., Tang L. H., Wolfgang C. L., Choti M. A., Velculescu V. E., Diaz L. A. Jr., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W., Hruban R. H., Papadopoulos N. (2011) DAXX/ATRX, MEN1, and mTOR pathway genes are frequently altered in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Science 331, 1199–1203 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao Y., Gao Z., Li L., Jiang X., Shan A., Cai J., Peng Y., Li Y., Jiang X., Huang X., Wang J., Wei Q., Qin G., Zhao J., Jin X., Liu L., Li Y., Wang W., Wang J., Ning G. (2013) Whole exome sequencing of insulinoma reveals recurrent T372R mutations in YY1. Nat. Commun. 4, 2810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

