Insights into the structure and function of membrane-integrated processive glycosyltransferases
- PMID: 26342143
- PMCID: PMC4684724
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2015.07.008
Insights into the structure and function of membrane-integrated processive glycosyltransferases
Abstract
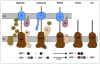
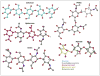
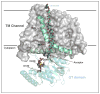
Complex carbohydrates perform essential functions in life, including energy storage, cell signaling, protein targeting, quality control, as well as supporting cell structure and stability. Extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) represent mainly structural polymers and are found in essentially all kingdoms of life. For example, EPS are important biofilm and capsule components in bacteria, represent major constituents in cell walls of fungi, algae, arthropods and plants, and modulate the extracellular matrix in vertebrates. Different mechanisms evolved by which EPS are synthesized. Here, we review the structures and functions of membrane-integrated processive glycosyltransferases (GTs) implicated in the synthesis and secretion of chitin, alginate, hyaluronan and poly-N-acetylglucosamine (PNAG).
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lairson LL, Henrissat B, Davies GJ, Withers SG. Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:521–555. A comprehensive review of the structures, functions and reaction mechanisms of glycosyltransferases. - PubMed
-
- McFarlane HE, Döring A, Persson S. The cell biology of cellulose synthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2014;65:69–94. - PubMed
-
- Morgan JLW, McNamara JT, Zimmer J. Mechanism of activation of bacterial cellulose synthase by cyclic di-GMP. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014;21:489–496. The structure of cyclic-di-GMP bound to bacterial cellulose synthase reveals how cyclic-di-GMP allosterically activates cellulose biosynthesis. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

