Twist promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in breast cancer cells through PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathways
- PMID: 26342198
- PMCID: PMC4694864
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4697
Twist promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in breast cancer cells through PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathways
Abstract
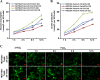
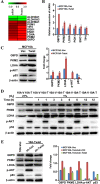
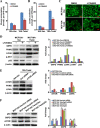
Twist, a key regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), plays an important role in the development of a tumorigenic phenotype. Energy metabolism reprogramming (EMR), a newly discovered hallmark of cancer cells, potentiates cancer cell proliferation, survival, and invasion. Currently little is known about the effects of Twist on tumor EMR. In this study, we found that glucose consumption and lactate production were increased and mitochondrial mass was decreased in Twist-overexpressing MCF10A mammary epithelial cells compared with vector-expressing MCF10A cells. Moreover, these Twist-induced phenotypic changes were augmented by hypoxia. The expression of some glucose metabolism-related genes such as PKM2, LDHA, and G6PD was also found to be upregulated. Mechanistically, activated β1-integrin/FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR and suppressed P53 signaling were responsible for the observed EMR. Knockdown of Twist reversed the effects of Twist on EMR in Twist-overexpressing MCF10A cells and Twist-positive breast cancer cells. Furthermore, blockage of the β1-integrin/FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway by siRNA or specific chemical inhibitors, or rescue of p53 activation can partially reverse the switch of glucose metabolism and inhibit the migration of Twist-overexpressing MCF10A cells and Twist-positive breast cancer cells. Thus, our data suggest that Twist promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in MCF10A-Twist cells and Twist-positive breast cancer cells via activation of the β1-integrin/FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and inhibition of the p53 pathway. Our study provides new insight into EMR.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT; Twist; glucose metabolism; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Twist induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell motility in breast cancer via ITGB1-FAK/ILK signaling axis and its associated downstream network.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Feb;71:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26693891
-
Alisertib induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR and sirtuin 1-mediated signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancer cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jan 17;9:575-601. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S75221. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25632225 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin induces expression of twist and cell motility via the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α translational pathway in colorectal cancer cells.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Apr;226(4):1060-8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22428. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20857420
-
Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 May;142(2):164-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24333502 Review.
-
AKT-ions with a TWIST between EMT and MET.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):62767-62777. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11232. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27623213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic rewiring in the promotion of cancer metastasis: mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Oncogene. 2020 Sep;39(39):6139-6156. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01432-7. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32839493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycolysis Reprogramming in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Unveiling the Mystery of Lactate in the Lung.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 25;25(1):315. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010315. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are Integrins Still Practicable Targets for Anti-Cancer Therapy?Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 12;11(7):978. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070978. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31336983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ITGB4-mediated metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(3):664-676. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1014-0. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31534187
-
Twist-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Confers Specific Metabolic and Mitochondrial Alterations.Cells. 2025 Jan 9;14(2):80. doi: 10.3390/cells14020080. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–314. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Pouyssegur J. Tumor cell metabolism: cancer's Achilles' heel. Cancer cell. 2008;13:472–482. - PubMed
-
- Mayevsky A. Mitochondrial function and energy metabolism in cancer cells: past overview and future perspectives. Mitochondrion. 2009;9:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira LM. Cancer metabolism: the Warburg effect today. Experimental and molecular pathology. 2010;89:372–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

