The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis: results from an international inception cohort study
- PMID: 26342222
- PMCID: PMC4939728
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev311
The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis: results from an international inception cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To determine nephritis outcomes in a prospective multi-ethnic/racial SLE inception cohort.
Methods: Patients in the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics inception cohort (≤15 months of SLE diagnosis) were assessed annually for estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), proteinuria and end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Health-related quality of life was measured by the Short Form (36 questions) health survey questionnaire (SF-36) subscales, mental and physical component summary scores.
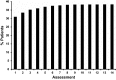
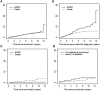
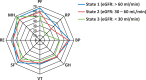
Results: There were 1827 patients, 89% females, mean (s.d.) age 35.1 (13.3) years. The mean (s.d.) SLE duration at enrolment was 0.5 (0.3) years and follow-up 4.6 (3.4) years. LN occurred in 700 (38.3%) patients: 566/700 (80.9%) at enrolment and 134/700 (19.1%) during follow-up. Patients with nephritis were younger, more frequently men and of African, Asian and Hispanic race/ethnicity. The estimated overall 10-year incidence of ESRD was 4.3% (95% CI: 2.8%, 5.8%), and with nephritis was 10.1% (95% CI: 6.6%, 13.6%). Patients with nephritis had a higher risk of death (HR = 2.98, 95% CI: 1.48, 5.99; P = 0.002) and those with eGFR <30 ml/min at diagnosis had lower SF-36 physical component summary scores (P < 0.01) and lower Physical function, Physical role and Bodily pain scores. Over time, patients with abnormal eGFR and proteinuria had lower SF-36 mental component summary (P ≤ 0.02) scores compared to patients with normal values.
Conclusion: LN occurred in 38.3% of SLE patients, frequently as the initial presentation, in a large multi-ethnic inception cohort. Despite current standard of care, nephritis was associated with ESRD and death, and renal insufficiency was linked to lower health-related quality of life. Further advances are required for the optimal treatment of LN.
Keywords: inception cohort; lupus; nephritis; outcomes research; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Outcome of lupus glomerulonephritis: the role of prospective observational cohort studies.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016 Feb;55(2):195-6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev220. Epub 2015 Sep 5. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 26342225 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rovin BH, Stillman I. Kidney. In: Lahita R, ed. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, 5th ed. San Diego, CA, USA: Academic Press, 2011: 769–814.
-
- Dooley MA. Clinical and epidemiologic features of lupus nephritis. In: Wallace DJ, Hahn BH, eds. Dubois’ Lupus Erythematosus and related syndromes. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier Saunders, 2013: 438–54.
-
- Croca SC, Rodrigues T, Isenberg DA. Assessment of a lupus nephritis cohort over a 30-year period. Rheumatology 2011;50:1424–30. - PubMed
-
- Houssiau F, Vasconcelos C, D’Cruz D, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy in lupus nephritis: the Euro-Lupus Nephritis Trial, a randomized trial of low-dose versus high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:2121–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

