The genetics of human autoimmune disease: A perspective on progress in the field and future directions
- PMID: 26343334
- PMCID: PMC4628839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.08.015
The genetics of human autoimmune disease: A perspective on progress in the field and future directions
Abstract
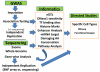
Progress in defining the genetics of autoimmune disease has been dramatically enhanced by large scale genetic studies. Genome-wide approaches, examining hundreds or for some diseases thousands of cases and controls, have been implemented using high throughput genotyping and appropriate algorithms to provide a wealth of data over the last decade. These studies have identified hundreds of non-HLA loci as well as further defining HLA variations that predispose to different autoimmune diseases. These studies to identify genetic risk loci are also complemented by progress in gene expression studies including definition of expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL), various alterations in chromatin structure including histone marks, DNase I sensitivity, repressed chromatin regions as well as transcript factor binding sites. Integration of this information can partially explain why particular variations can alter proclivity to autoimmune phenotypes. Despite our incomplete knowledge base with only partial definition of hereditary factors and possible functional connections, this progress has and will continue to facilitate a better understanding of critical pathways and critical changes in immunoregulation. Advances in defining and understanding functional variants potentially can lead to both novel therapeutics and personalized medicine in which therapeutic approaches are chosen based on particular molecular phenotypes and genomic alterations.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Functional variants; Genetics; HLA; Immunoregulation; Susceptibility loci.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Sundquist K, Martineus JC, Li X, Hemminki K, Sundquist J. Concordant and discordant associations between rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and ankylosing spondylitis based on all hospitalizations in Sweden between 1973 and 2004. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:1199–202. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mehers KL, Gillespie KM. The genetic basis for type 1 diabetes. British medical bulletin. 2008;88:115–29. - PubMed
-
- Korponay-Szabo I, Kovacs J, Lorincz M, Torok E, Goracz G. Families with multiple cases of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie. 1998;36:553–8. - PubMed
-
- Selmi C, Invernizzi P, Keefe EB, Coppel RL, Podda M, Rossaro L, et al. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38:264–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

