Helios, and not FoxP3, is the marker of activated Tregs expressing GARP/LAP
- PMID: 26343373
- PMCID: PMC4652984
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4771
Helios, and not FoxP3, is the marker of activated Tregs expressing GARP/LAP
Abstract
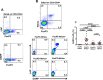
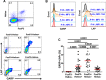
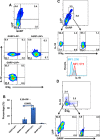
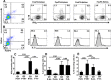
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are key players of immune regulation/dysregulation both in physiological and pathophysiological settings. Despite significant advances in understanding Treg function, there is still a pressing need to define reliable and specific markers that can distinguish different Treg subpopulations. Herein we show for the first time that markers of activated Tregs [latency associated peptide (LAP) and glycoprotein A repetitions predominant (GARP, or LRRC32)] are expressed on CD4+FoxP3- T cells expressing Helios (FoxP3-Helios+) in the steady state. Following TCR activation, GARP/LAP are up-regulated on CD4+Helios+ T cells regardless of FoxP3 expression (FoxP3+/-Helios+). We show that CD4+GARP+/-LAP+ Tregs make IL-10 immunosuppressive cytokine but not IFN-γ effector cytokine. Further characterization of FoxP3/Helios subpopulations showed that FoxP3+Helios+ Tregs proliferate in vitro significantly less than FoxP3+Helios- Tregs upon TCR stimulation. Unlike FoxP3+Helios- Tregs, FoxP3+Helios+ Tregs secrete IL-10 but not IFN-γ or IL-2, confirming they are bona fide Tregs with immunosuppressive characteristics. Taken together, Helios, and not FoxP3, is the marker of activated Tregs expressing GARP/LAP, and FoxP3+Helios+ Tregs have more suppressive characteristics, compared with FoxP3+Helios- Tregs. Our work implies that therapeutic modalities for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, allergies and graft rejection should be designed to induce and/or expand FoxP3+Helios+ Tregs, while therapies against cancers or infectious diseases should avoid such expansion/induction.
Keywords: FoxP3; GARP/LAP; Helios; Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; regulatory T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Elkord E, Alcantar-Orozco EM, Dovedi SJ, Tran DQ, Hawkins RE, Gilham DE. T regulatory cells in cancer: recent advances and therapeutic potential. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10:1573–1586. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM, Hafler DA. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:490–500. - PubMed
-
- von Boehmer H, Daniel C. Therapeutic opportunities for manipulating T(Reg) cells in autoimmunity and cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:51–63. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary B, Abd Al Samid M, al-Ramadi BK, Elkord E. Phenotypic alterations, clinical impact and therapeutic potential of regulatory T cells in cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14:931–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

