Detection of Selection Signatures on the X Chromosome in Three Sheep Breeds
- PMID: 26343642
- PMCID: PMC4613208
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160920360
Detection of Selection Signatures on the X Chromosome in Three Sheep Breeds
Abstract
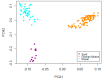
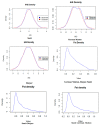
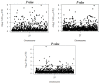
Artificial selection has played a critical role in animal breeding. Detection of artificial selection footprints in genomic regions can provide insights for understanding the function of specific phenotypic traits and better guide animal breeding. To more fully understand the relationship between genomic composition and phenotypic diversity arising from breed development, a genome-wide scan was conducted using an OvineSNP50 BeadChip and integrated haplotype score and fixation index analyses to detect selection signatures on the X chromosome in three sheep breeds. We identified 49, 34, and 55 candidate selection regions with lengths of 27.49, 16.47, and 25.42 Mb in German Mutton, Dorper, and Sunit sheep, respectively. Bioinformatics analysis showed that some of the genes in these regions with selection signatures, such as BMP15, were relevant to reproduction. We also identified some selection regions harboring genes that had human orthologs, including BKT, CENPI, GUCY2F, MSN, PCDH11X, PLP1, VSIG4, PAK3, WAS, PCDH19, PDHA1, and SRPX2. The VSIG4 and PCDH11X genes are associated with the immune system and disease, PDHA1 is associated with biosynthetic related pathways, and PCDH19 is expressed in the nervous system and skin. These genes may be useful as candidate genes for molecular breeding.
Keywords: X chromosome; selection signature; sheep.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A selection signatures study among Middle Eastern and European sheep breeds.J Anim Breed Genet. 2021 Sep;138(5):574-588. doi: 10.1111/jbg.12536. Epub 2021 Jan 16. J Anim Breed Genet. 2021. PMID: 33453096
-
Genome-wide scan for selection signatures in six cattle breeds in South Africa.Genet Sel Evol. 2015 Nov 26;47:92. doi: 10.1186/s12711-015-0173-x. Genet Sel Evol. 2015. PMID: 26612660 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis reveals signatures of selection for important traits in domestic sheep from different ecoregions.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 3;17(1):863. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3212-2. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27809776 Free PMC article.
-
The study of selection signature and its applications on identification of candidate genes using whole genome sequencing data in chicken-a review.Poult Sci. 2023 Jun;102(6):102657. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102657. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37054499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of the phenotypic evolution in sheep: a molecular look at diversity-driving genes.Genet Sel Evol. 2022 Sep 9;54(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12711-022-00753-3. Genet Sel Evol. 2022. PMID: 36085023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scanning of selection signature provides a glimpse into important economic traits in goats (Capra hircus).Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 31;6:36372. doi: 10.1038/srep36372. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796358 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Selection Signals on the X-Chromosome in East Adriatic Sheep: A New Complementary Approach.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 11;13:887582. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.887582. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35615375 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing genetic architecture and signatures of selection of dual purpose Gir cattle populations using genomic information.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 2;13(8):e0200694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200694. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30071036 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling genomic regions that underlie differences between Afec-Assaf sheep and its parental Awassi breed.Genet Sel Evol. 2017 Feb 10;49(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12711-017-0296-3. Genet Sel Evol. 2017. PMID: 28187715 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the genomic regions of selection on the X chromosome in different cattle breeds.3 Biotech. 2024 Feb;14(2):50. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03905-4. Epub 2024 Jan 22. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38268984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kijas J.W., Lenstra J.A., Hayes B., Boitard S., Neto L.P., Cristobal M.S., Servin B., McCulloch R., Whan V., Gietzen K., et al. Genome-wide analysis of the world’s sheep breeds reveals high levels of historic mixture and strong recent selection. PLoS Biol. 2012;10 doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001258. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao F., Wei C., Zhang L., Liu J., Wang G., Zeng T., Du L. A genome scan of recent positive selection signatures in three sheep populations. J. Integr. Agric. 2015;15 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61080-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

