Structural Conservation and Functional Diversity of the Poxvirus Immune Evasion (PIE) Domain Superfamily
- PMID: 26343707
- PMCID: PMC4584292
- DOI: 10.3390/v7092848
Structural Conservation and Functional Diversity of the Poxvirus Immune Evasion (PIE) Domain Superfamily
Abstract
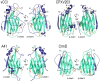
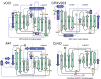
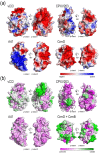
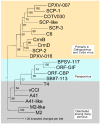
Poxviruses encode a broad array of proteins that serve to undermine host immune defenses. Structural analysis of four of these seemingly unrelated proteins revealed the recurrent use of a conserved beta-sandwich fold that has not been observed in any eukaryotic or prokaryotic protein. Herein we propose to call this unique structural scaffolding the PIE (Poxvirus Immune Evasion) domain. PIE domain containing proteins are abundant in chordopoxvirinae, with our analysis identifying 20 likely PIE subfamilies among 33 representative genomes spanning 7 genera. For example, cowpox strain Brighton Red appears to encode 10 different PIEs: vCCI, A41, C8, M2, T4 (CPVX203), and the SECRET proteins CrmB, CrmD, SCP-1, SCP-2, and SCP-3. Characterized PIE proteins all appear to be nonessential for virus replication, and all contain signal peptides for targeting to the secretory pathway. The PIE subfamilies differ primarily in the number, size, and location of structural embellishments to the beta-sandwich core that confer unique functional specificities. Reported ligands include chemokines, GM-CSF, IL-2, MHC class I, and glycosaminoglycans. We expect that the list of ligands and receptors engaged by the PIE domain will grow as we come to better understand how this versatile structural architecture can be tailored to manipulate host responses to infection.
Keywords: PIE domain; SECRET domain; chemokine and cytokine decoy receptors; poxvirus; viral immune evasion.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Poxvirus genomes encode a secreted, soluble protein that preferentially inhibits beta chemokine activity yet lacks sequence homology to known chemokine receptors.Virology. 1997 Sep 29;236(2):316-27. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8730. Virology. 1997. PMID: 9325239
-
Immunology 101 at poxvirus U: immune evasion genes.Semin Immunol. 2001 Feb;13(1):59-66. doi: 10.1006/smim.2000.0296. Semin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11289800 Review.
-
Poxvirus-encoded TNF decoy receptors inhibit the biological activity of transmembrane TNF.J Gen Virol. 2015 Oct;96(10):3118-3123. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000255. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Gen Virol. 2015. PMID: 26242179
-
Poxvirus Immune Evasion.Annu Rev Immunol. 2024 Jun;42(1):551-584. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-090222-110227. Annu Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38941604 Review.
-
Subversion of cytokine networks by virally encoded decoy receptors.Immunol Rev. 2012 Nov;250(1):199-215. doi: 10.1111/imr.12009. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23046131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The genomes of three North American orthopoxviruses.Virus Genes. 2017 Feb;53(1):21-34. doi: 10.1007/s11262-016-1388-9. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Virus Genes. 2017. PMID: 27613417
-
Exploring the genomic basis of Mpox virus-host transmission and pathogenesis.mSphere. 2024 Dec 19;9(12):e0057624. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00576-24. Epub 2024 Nov 14. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39540739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of GM-CSF and IL-2 sequestration by the viral decoy receptor GIF.Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 7;7:13228. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13228. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27819269 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the immunomodulatory properties of poxvirus cytokine decoy receptors at the cell surface.F1000Res. 2018 Jun 11;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-719. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.14238.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 29946427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNF Decoy Receptors Encoded by Poxviruses.Pathogens. 2021 Aug 22;10(8):1065. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10081065. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34451529 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jackson S.S., Ilyinskii P., Philippon V., Gritz L., Yafal A.G., Zinnack K., Beaudry K.R., Manson K.H., Lifton M.A., Kuroda M.J., et al. Role of Genes That Modulate Host Immune Responses in the Immunogenicity and Pathogenicity of Vaccinia Virus. J. Virol. 2005;79:6554–6559. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.10.6554-6559.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Werden S.J., Rahman M.M., McFadden G. Poxvirus Host Range Genes. Adv. Virus Res. 2008;71:135–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

