Identification and analysis of the N(6)-methyladenosine in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcriptome
- PMID: 26343792
- PMCID: PMC4561376
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13859
Identification and analysis of the N(6)-methyladenosine in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcriptome
Abstract
Knowledge of the distribution of N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is invaluable for understanding RNA biological functions. However, limitation in experimental methods impedes the progress towards the identification of m(6)A site. As a complement of experimental methods, a support vector machine based-method is proposed to identify m(6)A sites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. In this model, RNA sequences are encoded by their nucleotide chemical property and accumulated nucleotide frequency information. It is observed in the jackknife test that the accuracy achieved by the proposed model in identifying the m(6)A site was 78.15%. For the convenience of experimental scientists, a web-server for the proposed model is provided at http://lin.uestc.edu.cn/server/m6Apred.php.
Figures
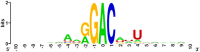
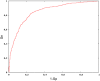

Similar articles
-
RAMPred: identifying the N(1)-methyladenosine sites in eukaryotic transcriptomes.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 11;6:31080. doi: 10.1038/srep31080. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27511610 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying N 6-methyladenosine sites in the Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome.Mol Genet Genomics. 2016 Dec;291(6):2225-2229. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1243-7. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Mol Genet Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27590733
-
Detecting N6-methyladenosine sites from RNA transcriptomes using ensemble Support Vector Machines.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 12;7:40242. doi: 10.1038/srep40242. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28079126 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison and Analysis of Computational Methods for Identifying N6-Methyladenosine Sites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(9):1219-1229. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201109110703. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33167827 Review.
-
Analysis approaches for the identification and prediction of N6-methyladenosine sites.Epigenetics. 2023 Dec;18(1):2158284. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2158284. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 36562485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
iLearnPlus: a comprehensive and automated machine-learning platform for nucleic acid and protein sequence analysis, prediction and visualization.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 4;49(10):e60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab122. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33660783 Free PMC article.
-
6mA-StackingCV: an improved stacking ensemble model for predicting DNA N6-methyladenine site.BioData Min. 2023 Nov 27;16(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13040-023-00348-8. BioData Min. 2023. PMID: 38012796 Free PMC article.
-
RNA modifications in aging-associated cardiovascular diseases.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Sep 29;14(19):8110-8136. doi: 10.18632/aging.204311. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36178367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SkipCPP-Pred: an improved and promising sequence-based predictor for predicting cell-penetrating peptides.BMC Genomics. 2017 Oct 16;18(Suppl 7):742. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4128-1. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29513192 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning applications in RNA modification sites prediction.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Sep 29;19:5510-5524. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.09.025. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34712397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

