Potential role of the IL-33/ST2 axis in celiac disease
- PMID: 26343805
- PMCID: PMC5360881
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2015.85
Potential role of the IL-33/ST2 axis in celiac disease
Abstract
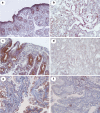
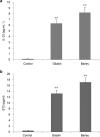
The IL-33/ST2 axis has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several tissue-specific autoimmune diseases. Celiac disease (CD) is the only autoimmune disease in which both the major genetic factors (HLA-DQ2/DQ8) and etiologic ones (dietary gluten) for susceptibility are known. We have measured serum levels and determined intestinal tissue expression of IL-33 and its receptor soluble ST2 in patients with CD to investigate their association with disease activity. Serum and tissue levels of both IL-33 and sST2 were significantly higher in patients with CD compared with those in control patients without CD. We show that toxic peptides extracted from barley and wheat gliadin significantly stimulate the production of IL-33 and ST2 in cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cell from celiac patients, strongly implicating the IL-33/ST2 axis in the pathogenesis of CD. The higher levels of IL-33 and its receptor ST2 in tissue and serum reflect an active inflammatory state and may represent a potential biomarker for disease activity. A better understanding of IL-33/ST2 release, mode of action, and regulation will be crucial to develop therapeutics that target the IL-33/ST2 pathway to treat CD.Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, 7 September 2015; doi:10.1038/cmi.2015.85.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Interleukin-33/ST2 Pathway Is Expressed in the Failing Human Heart and Associated with Pro-fibrotic Remodeling of the Myocardium.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2018 Feb;11(1):15-21. doi: 10.1007/s12265-017-9775-8. Epub 2017 Dec 28. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29285671 Free PMC article.
-
The interleukin-33 receptor ST2 is important for the development of peripheral airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a house dust mite mouse model of asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2016 Mar;46(3):479-90. doi: 10.1111/cea.12683. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016. PMID: 26609909
-
ST2 and the ST2/IL-33 signalling pathway-biochemistry and pathophysiology in animal models and humans.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Aug;495:493-500. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 May 25. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31136737 Review.
-
Effects of IL-33/ST2 pathway in acute inflammation on tissue damage, antioxidative parameters, magnesium concentration and cytokines profile.Exp Mol Pathol. 2016 Aug;101(1):31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 May 21. Exp Mol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27222019
-
IL-33/ST2 Pathway as a Rational Therapeutic Target for CNS Diseases.Neuroscience. 2018 Jan 15;369:222-230. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.11.028. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29175156 Review.
Cited by
-
Celiac Disease Causes Epithelial Disruption and Regulatory T Cell Recruitment in the Oral Mucosa.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:623805. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.623805. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717129 Free PMC article.
-
A Deep View of the Biological Property of Interleukin-33 and Its Dysfunction in the Gut.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 31;24(17):13504. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713504. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coexistence of apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis pathways in celiac disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Dec 13;214(3):328-340. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad082. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37455655 Free PMC article.
-
Interference of LPS H. pylori with IL-33-Driven Regeneration of Caviae porcellus Primary Gastric Epithelial Cells and Fibroblasts.Cells. 2021 Jun 4;10(6):1385. doi: 10.3390/cells10061385. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34199843 Free PMC article.
-
Proregenerative Activity of IL-33 in Gastric Tissue Cells Undergoing Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 5;21(5):1801. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051801. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32151084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sollid LM. Celiac disease: dissecting a complex inflammatory disorder. Nat Rev Immunol 2000; 2: 647–655. - PubMed
-
- Alaedini A, Green PH. Narrative review: celiac disease: understanding a complex autoimmune disorder. Ann Intern Med 2005; 142: 289–298. - PubMed
-
- Torres MI, López-Casado MA, Luque J, Peña J, Ríos A. New advances in celiac disease: serum and intestinal expression of HLA-G. Int Immunol 2006; 18: 713–718. - PubMed
-
- Fasano A. Clinical presentation of celiac disease in the pediatric population. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: S68–S73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

