A Modified Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Vaccine with Reduced Activity of Antioxidants and Glutamine Synthetase Exhibits Enhanced Protection of Mice despite Diminished in Vivo Persistence
- PMID: 26343849
- PMCID: PMC4552197
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines1010034
A Modified Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Vaccine with Reduced Activity of Antioxidants and Glutamine Synthetase Exhibits Enhanced Protection of Mice despite Diminished in Vivo Persistence
Abstract
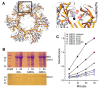
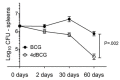
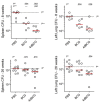
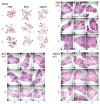
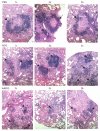
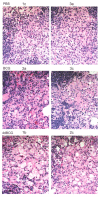
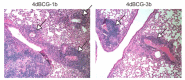
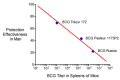
Early attempts to improve BCG have focused on increasing the expression of prominent antigens and adding recombinant toxins or cytokines to influence antigen presentation. One such modified BCG vaccine candidate has been withdrawn from human clinical trials due to adverse effects. BCG was derived from virulent Mycobacterium bovis and retains much of its capacity for suppressing host immune responses. Accordingly, we have used a different strategy for improving BCG based on reducing its immune suppressive capacity. We made four modifications to BCG Tice to produce 4dBCG and compared it to the parent vaccine in C57Bl/6 mice. The modifications included elimination of the oxidative stress sigma factor SigH, elimination of the SecA2 secretion channel, and reductions in the activity of iron co-factored superoxide dismutase and glutamine synthetase. After IV inoculation of 4dBCG, 95% of vaccine bacilli were eradicated from the spleens of mice within 60 days whereas the titer of BCG Tice was not significantly reduced. Subcutaneous vaccination with 4dBCG produced greater protection than vaccination with BCG against dissemination of an aerosolized challenge of M. tuberculosis to the spleen at 8 weeks post-challenge. At this time, 4dBCG-vaccinated mice also exhibited altered lung histopathology compared to BCG-vaccinated mice and control mice with less well-developed lymphohistiocytic nodules in the lung parenchyma. At 26 weeks post-challenge, 4dBCG-vaccinated mice but not BCG-vaccinated mice had significantly fewer challenge bacilli in the lungs than control mice. In conclusion, despite reduced persistence in mice a modified BCG vaccine with diminished antioxidants and glutamine synthetase is superior to the parent vaccine in conferring protection against M. tuberculosis. The targeting of multiple immune suppressive factors produced by BCG is a promising strategy for simultaneously improving vaccine safety and effectiveness.
Keywords: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG); antioxidants; glutamine synthetase; immune suppression; immunity; sigma factor; superoxide dismutase; tuberculosis; vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reducing the activity and secretion of microbial antioxidants enhances the immunogenicity of BCG.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005531. Epub 2009 May 13. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19436730 Free PMC article.
-
Oral delivery of lipid-encapsulated Mycobacterium bovis BCG extends survival of the bacillus in vivo and induces a long-term protective immune response against tuberculosis.Vaccine. 2006 Mar 15;24(12):2071-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.11.017. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 16332403
-
[Novel vaccines against M. tuberculosis].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):745-51. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240920 Review. Japanese.
-
Protection by novel vaccine candidates, Mycobacterium tuberculosis ΔmosR and ΔechA7, against challenge with a Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing strain.Vaccine. 2015 Oct 13;33(42):5633-5639. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.08.084. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26363381 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects in Mycobacterium bovis Bacille Calmette et Guérin (BCG) vaccine diversity and delivery: why does BCG fail to protect against tuberculosis?Vaccine. 2015 Sep 22;33(39):5035-41. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.08.033. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26319069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vaccine-elicited memory CD4+ T cell expansion is impaired in the lungs during tuberculosis.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Nov 27;13(11):e1006704. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006704. eCollection 2017 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29176787 Free PMC article.
-
Morphology of Lymphoid Tissue in the Lungs of Guinea Pigs Infected with Mycobacterium bovis against the Background of Vaccine Immunity and the Action of Betulin and Its Derivatives.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 6;10(12):2084. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122084. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560494 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant BCG to Enhance Its Immunomodulatory Activities.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 May 23;10(5):827. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10050827. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35632582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fine P.E.M., Carneiro I.A.M., Milstien J.B., Clements J.D. Issues Relating to the Use of BCG in Immunization Programs, a Discussion Document, Document WHO/V&B/99.23 ed. World Health Organization Department of Vaccines and Biologicals; Geneva, Switzerland: 1999.
-
- Trunz B.B., Fine P., Dye C. Effect of BCG vaccination on childhood tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis worldwide: A meta-analysis and assessment of cost-effectiveness. Lancet. 2006;367:1173–1180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

