Detection of Bulky Endogenous Oxidative DNA Lesions Derived from 8,5'-Cyclo-2'-deoxyadenosine by ³²P-Postlabeling Assay
- PMID: 26344223
- PMCID: PMC4562074
- DOI: 10.1002/0471140856.tx1717s64
Detection of Bulky Endogenous Oxidative DNA Lesions Derived from 8,5'-Cyclo-2'-deoxyadenosine by ³²P-Postlabeling Assay
Abstract
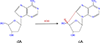
8,5'-Cyclopurine-2'-deoxynucleotides represent a class of oxidative DNA lesions that are specifically repaired by nucleotide excision repair but not by base excision repair or direct enzymatic reversion. The 32P-postlabeling assay is an ultrasensitive method that has been extensively used for the detection of carcinogen-DNA adducts in laboratory animal and epidemiological studies. This assay under modified chromatographic conditions is also a suitable and sensitive method for the detection of 8,5'-cyclo-2'-deoxyadenosine (cA). After enzymatic digestion of DNA, and enrichment of the oxidative products from the DNA digest, four dinucleotides containing cA, i.e., Ap-cAp, Cp-cAp, Gp-cAp, and Tp-cAp, are 5'-labeled with [32P]orthophosphate from [γ-32P]ATP, mediated by polynucleotide kinase (PNK). The 32P-labeled cA products are separated by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and quantified by Instant Imager or by a scintillation counter. The assay only requires 1 to 10 μg of DNA sample and is capable of detecting cA lesions at frequencies as low as 1 in 1010 normal nucleotides. © 2015 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Keywords: 32P-postlabeling assay; 8,5′-cyclopurine-2′-deoxynucleotides; oxidative DNA damage; thin-layer chromatography.
Copyright © 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Chang J, Jaeschke H, Randerath K. Effect of Ni(II) on tissue hydrogen peroxide content in mice as inferred from glutathione and glutathione disulfide measurements. Life Sci. 1994;55:1789–1796. - PubMed
-
- Chatgilialoglu C, Ferreri C, Terzidis MA. Purine 5',8-cyclonucleoside lesions: chemistry and biology. Chemical Society reviews. 2011;40:1368–1382. - PubMed
-
- De Bont R, van Larebeke N. Endogenous DNA damage in humans: a review of quantitative data. Mutagenesis. 2004;19:169–185. - PubMed
-
- Dizdaroglu M. Oxidative damage to DNA in mammalian chromatin. Mutation research. 1992;275:331–342. - PubMed
-
- Everson RB, Randerath E, Santella RM, Cefalo RC, Avitts TA, Randerath K. Detection of smoking-related covalent DNA adducts in human placenta. Science (New York, N.Y. 1986;231:54–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

