Network structure of brain atrophy in de novo Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 26344547
- PMCID: PMC4596689
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.08440
Network structure of brain atrophy in de novo Parkinson's disease
Abstract
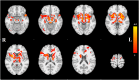
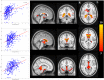
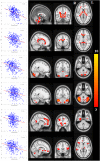
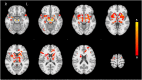
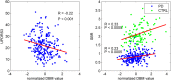
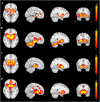
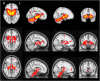
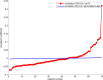
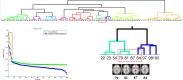
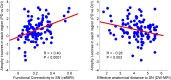
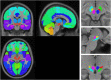
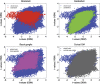
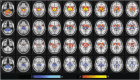
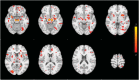
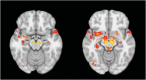
We mapped the distribution of atrophy in Parkinson's disease (PD) using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and clinical data from 232 PD patients and 117 controls from the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative. Deformation-based morphometry and independent component analysis identified PD-specific atrophy in the midbrain, basal ganglia, basal forebrain, medial temporal lobe, and discrete cortical regions. The degree of atrophy reflected clinical measures of disease severity. The spatial pattern of atrophy demonstrated overlap with intrinsic networks present in healthy brain, as derived from functional MRI. Moreover, the degree of atrophy in each brain region reflected its functional and anatomical proximity to a presumed disease epicenter in the substantia nigra, compatible with a trans-neuronal spread of the disease. These results support a network-spread mechanism in PD. Finally, the atrophy pattern in PD was also seen in healthy aging, where it also correlated with the loss of striatal dopaminergic innervation.
Keywords: MRI; basal ganglia; deformation-based morphometry; human; independent component analysis; neuroscience; substantia nigra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Apostolova LG, Beyer M, Green AE, Hwang KS, Morra JH, Chou YY, Avedissian C, Aarsland D, Janvin CC, Larsen JP, Cummings JL, Thompson PM. Hippocampal, caudate, and ventricular changes in Parkinson's disease with and without dementia. Movement Disorders. 2010;25:687–695. doi: 10.1002/mds.22799. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aubert-Broche B, Fonov VS, García-Lorenzo D, Mouiha A, Guizard N, Coupé P, Eskildsen SF, Collins DL. A new method for structural volume analysis of longitudinal brain MRI data and its application in studying the growth trajectories of anatomical brain structures in childhood. Neuroimage. 2013;82:393–402. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.065. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

