Peptide Vaccine: Progress and Challenges
- PMID: 26344743
- PMCID: PMC4494216
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines2030515
Peptide Vaccine: Progress and Challenges
Abstract
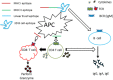
Conventional vaccine strategies have been highly efficacious for several decades in reducing mortality and morbidity due to infectious diseases. The bane of conventional vaccines, such as those that include whole organisms or large proteins, appear to be the inclusion of unnecessary antigenic load that, not only contributes little to the protective immune response, but complicates the situation by inducing allergenic and/or reactogenic responses. Peptide vaccines are an attractive alternative strategy that relies on usage of short peptide fragments to engineer the induction of highly targeted immune responses, consequently avoiding allergenic and/or reactogenic sequences. Conversely, peptide vaccines used in isolation are often weakly immunogenic and require particulate carriers for delivery and adjuvanting. In this article, we discuss the specific advantages and considerations in targeted induction of immune responses by peptide vaccines and progresses in the development of such vaccines against various diseases. Additionally, we also discuss the development of particulate carrier strategies and the inherent challenges with regard to safety when combining such technologies with peptide vaccines.
Keywords: adjuvants; epitope; peptide vaccine.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

