Vaccinia Virus LC16m8∆ as a Vaccine Vector for Clinical Applications
- PMID: 26344890
- PMCID: PMC4494248
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines2040755
Vaccinia Virus LC16m8∆ as a Vaccine Vector for Clinical Applications
Abstract
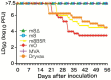
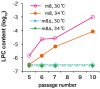
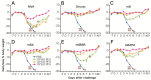
The LC16m8 strain of vaccinia virus, the active ingredient in the Japanese smallpox vaccine, was derived from the Lister/Elstree strain. LC16m8 is replication-competent and has been administered to over 100,000 infants and 3,000 adults with no serious adverse reactions. Despite this outstanding safety profile, the occurrence of spontaneously-generated large plaque-forming virulent LC16m8 revertants following passage in cell culture is a major drawback. We identified the gene responsible for the reversion and deleted the gene (B5R) from LC16m8 to derive LC16m8Δ. LC16m8∆ is non-pathogenic in immunodeficient severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice, genetically-stable and does not reverse to a large-plaque phenotype upon passage in cell culture, even under conditions in which most LC16m8 populations are replaced by revertants. Moreover, LC16m8∆ is >500-fold more effective than the non-replicating vaccinia virus (VV), Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA), at inducing murine immune responses against pathogenic VV. LC16m8∆, which expresses the SIV gag gene, also induced anti-Gag CD8⁺ T-cells more efficiently than MVA and another non-replicating VV, Dairen I minute-pock variants (DIs). Moreover, LC16m8∆ expressing HIV-1 Env in combination with a Sendai virus vector induced the production of anti-Env antibodies and CD8⁺ T-cells. Thus, the safety and efficacy of LC16m8∆ mean that it represents an outstanding platform for the development of human vaccine vectors.
Keywords: B5R; DIs; HIV; LC16m8; LC16m8∆; MVA; SIV; reversion; vaccinia virus.
Figures
References
-
- Fenner F., Henderson D.A., Arita I., Jezek Z., Ladnyi I.D., Organization W.H. Smallpox and Its Eradication. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 1988.
-
- Henderson D.A., Inglesby T.V., Bartlett J.G., Ascher M.S., Eitzen E., Jahrling P.B., Hauer J., Layton M., McDade J., Osterholm M.T., et al. Smallpox as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. Working group on civilian biodefense. JAMA. 1999;281:2127–2137. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.22.2127. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Multistate outbreak of monkeypox—Illinois, indiana, and wisconsin, 2003. JAMA. 2003;290:30–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

