Immunoregulation on Mice of Low Immunity and Effects on Five Kinds of Human Cancer Cells of Panax japonicus Polysaccharide
- PMID: 26345429
- PMCID: PMC4539973
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/839697
Immunoregulation on Mice of Low Immunity and Effects on Five Kinds of Human Cancer Cells of Panax japonicus Polysaccharide
Abstract
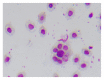
The goal of this study is to investigate the immunoregulative effects of Panax japonicus polysaccharide (PJPS) on mice of low immunity. An orthogonal experiment was designed to determine the best extraction process for PJPS. By the tests of macrophages swallow chicken red blood cells, Delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH), and serum hemolysin value, we studied the immune adjustment ability of PJPS. MTT was employed to detect the effects of different concentrations of PJPS, respectively, in 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h on five kinds of human cancer cells. The results show that the best extraction process for PJPS was as follows: ratio of solvent consumption to raw material 40, extraction temperature 100°C, re-extracted two times, each extraction time 4 hours. PJPS can significantly improve the immune function of mice processed by cyclophosphamide and PJPS did not work on the above five cancer cells.
Figures
References
-
- Du Z. X. Pharmaceutical Botany. People’s Medical Publishing House; 2009.
-
- Wang P. Study on the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of Panax japonicus . Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2007;25(12):17–19.
-
- Wen D. J., Zhang C. L., Chen G. D., Dong X. G., Xiao B. J. Study on the analgesic effects of total Panax japonicus Saponins. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research. 2008;19(8):1983–1984.
-
- Yuan J. The protective of panax japonicus saponins on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in dogs. Journal of Medicine and Pharmacy of Chinese Minorities. 2008;3:48–50.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources