An iso-15 : 0 O-alkylglycerol moiety is the key structure of the E-signal in Myxococcus xanthus
- PMID: 26346537
- PMCID: PMC4772708
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.000169
An iso-15 : 0 O-alkylglycerol moiety is the key structure of the E-signal in Myxococcus xanthus
Abstract
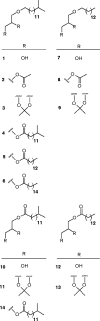
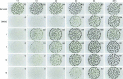
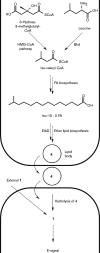
The E-signal is one of five intercellular signals (named A- to E-signal) guiding fruiting body development in Myxococcus xanthus, and it has been shown to be a combination of the branched-chain fatty acid (FA) iso-15 : 0 and the diacylmonoalkyl ether lipid TG1. Developmental mutants HB015 (Δbkd MXAN_4265::kan) and elbD (MXAN_1528::kan) are blocked at different stages of fruiting body and spore formation as they cannot form the required iso-FA or the actual ether lipid, respectively. In order to define the structural basis of the E-signal, different mono- and triglycerides containing ether or ester bonds were synthesized and used for complementation of these mutants. Here, the monoalkylglyceride dl-1-O-(13-methyltetradecyl)glycerol exhibited comparably high levels of complementation in both mutants, restoring fruiting body and spore formation, identifying iso-15 : 0 O-alkylglycerol, part of the natural lipid TG1, as the 'signalophore' of E-signalling.
Figures


References
-
- Bode H. B., Ring M. W., Schwär G., Kroppenstedt R. M., Kaiser D., Müller R. (2006). 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthase is involved in biosynthesis of isovaleryl-CoA in the myxobacterium Myxococcus xanthus during fruiting body formation J Bacteriol 188 6524–6528 10.1128/JB.00825-06 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bode H. B., Ring M. W., Schwär G., Altmeyer M. O., Kegler C., Jose I. R., Singer M., Müller R. (2009). Identification of additional players in the alternative biosynthesis pathway to isovaleryl-CoA in the myxobacterium Myxococcus xanthus ChemBioChem 10 128–140 10.1002/cbic.200800219 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

