Is the ratio of apoB/apoA-1 the best predictor for the severity of coronary artery lesions in Chinese diabetics with stable angina pectoris? An assessment based on Gensini scores
- PMID: 26346771
- PMCID: PMC4554779
- DOI: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2015.04.012
Is the ratio of apoB/apoA-1 the best predictor for the severity of coronary artery lesions in Chinese diabetics with stable angina pectoris? An assessment based on Gensini scores
Abstract
Background: There is a paucity of data about the best lipid ratio predicting the severity of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with diabetes mellitus. We determined the relationship between five conventional lipid ratios and the extent of coronary artery lesions in Chinese Type 2 diabetics with stable angina pectoris (SAP).
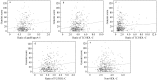
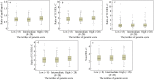
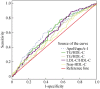
Methods: A prospective cohort study within 373 type 2 diabetic patients diagnosed with stable CAD by coronary angiography was performed. All patients were classified into three groups according to the tertiles of Gensini scores (GS, low group < 8 points n = 143; intermediate group 8-28 points, n = 109; high group > 28 points, n = 121). Association between the ratios of apolipoprotein (apo) B and apoA-1, total cholesterol and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (TC/HDL-C), triglycerides and HDL-C (TG/HDL-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol and HDL-C (LDL-C/HDL-C), Non-HDL-C/HDL-C and GS were evaluated using the receivers operating characteristic (ROC) curves and multivariate logistic regression models.
Results: The ratio of apoB/apoA-1, TC/HDL-C, LDL-C/HDL-C, and Non-HDL-C/HDL-C were correlated with Gensini scores. Area under the ROC curves for predicting high Gensini scores in the ratios of apoB/apoA-1, TC/HDL-C, LDL-C/HDL-C and Non-HDL-C/HDL-C were 0.62, 0.60, 0.59 and 0.60, respectively (P < 0.005 for all). According to multivariate logistic regression analysis after adjusted with demographic characteristic and other lipid parameters, the ratio of apoB/apoA-1 is qualified as an independent discriminator for the severity of CAD. However, after further adjusting different baseline variables, such as left ventricular ejective fraction, hemoglobin A1c, leukocytes count and serum creatinine, none of the above lipid ratios remained.
Conclusions: Compared with other lipid parameters, the ratio of apoB/apoA-1 appears to be more significantly correlated with the extent of coronary artery lesions in Chinese diabetics, but it was not an independent predictor in these settings.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Diabetic mellitus; Gensini scores; Lipid disorder.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship of lipid and lipoprotein ratios with coronary severity in patients with new on-set coronary artery disease complicated with type 2 diabetics.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2016 Aug;13(8):685-692. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2016.08.007. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27781059 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio combined with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Mar;34(3):274-279. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211008-01441. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35574745 Chinese.
-
Associations of lipid measures with total occlusion in patients with established coronary artery disease: a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Nov 11;21(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01733-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36369093 Free PMC article.
-
Age, Sex, and Cardiovascular Risk Attributable to Lipoprotein Cholesterol Among Chinese Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease: A Case-Control Study.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2019 May;17(4):223-231. doi: 10.1089/met.2018.0067. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 30720383
-
Association between paraoxonase-1 activity and lipid peroxidation indicator levels in people living in the Antalya region with angiographically documented coronary artery disease.Clin Cardiol. 2004 Jul;27(7):426-30. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960270714. Clin Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15298047 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship of lipid and lipoprotein ratios with coronary severity in patients with new on-set coronary artery disease complicated with type 2 diabetics.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2016 Aug;13(8):685-692. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2016.08.007. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27781059 Free PMC article.
-
Improved plaque neovascularization following 2-year atorvastatin therapy based on contrast-enhanced ultrasonography: A pilot study.Exp Ther Med. 2018 May;15(5):4491-4497. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5926. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29725384 Free PMC article.
-
Japan Atherosclerosis Society (JAS) Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases 2017.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018 Sep 1;25(9):846-984. doi: 10.5551/jat.GL2017. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018. PMID: 30135334 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Japan Atherosclerosis Society (JAS) Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases 2022.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Jun 1;31(6):641-853. doi: 10.5551/jat.GL2022. Epub 2023 Dec 19. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 38123343 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparison of three non-insulin-based insulin resistance indexes in predicting the presence and severity of coronary artery disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 29;9:918359. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.918359. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35966520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maxfield FR, Tabas I. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 2005;438:612–621. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1685–1695. - PubMed
-
- Reiner Z, Catapano AL, De Backer G, et al. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1769–1818. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
