Binary Logistic Regression Analysis of Foramen Magnum Dimensions for Sex Determination
- PMID: 26346917
- PMCID: PMC4540976
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/459428
Binary Logistic Regression Analysis of Foramen Magnum Dimensions for Sex Determination
Abstract
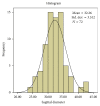
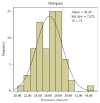
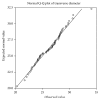
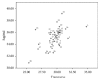
Purpose. The structural integrity of foramen magnum is usually preserved in fire accidents and explosions due to its resistant nature and secluded anatomical position and this study attempts to determine its sexing potential. Methods. The sagittal and transverse diameters and area of foramen magnum of seventy-two skulls (41 male and 31 female) from south Indian population were measured. The analysis was done using Student's t-test, linear correlation, histogram, Q-Q plot, and Binary Logistic Regression (BLR) to obtain a model for sex determination. The predicted probabilities of BLR were analysed using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve. Result. BLR analysis and ROC curve revealed that the predictability of the dimensions in sexing the crania was 69.6% for sagittal diameter, 66.4% for transverse diameter, and 70.3% for area of foramen. Conclusion. The sexual dimorphism of foramen magnum dimensions is established. However, due to considerable overlapping of male and female values, it is unwise to singularly rely on the foramen measurements. However, considering the high sex predictability percentage of its dimensions in the present study and the studies preceding it, the foramen measurements can be used to supplement other sexing evidence available so as to precisely ascertain the sex of the skeleton.
Figures







References
-
- Rogers T. L. Determining the sex of human remains through cranial morphology. Journal of Forensic Sciences. 2005;50(3):493–500. - PubMed
-
- Holland T. D. Use of the cranial base in the identification of fire victims. Journal of Forensic Sciences. 1989;34(2):458–460. - PubMed
-
- Sendemir E., Savci G., Cimen A. Evaluation of the foramen magnum dimensions. Acta Anatomica Nipponica. 1994;69(1):50–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

